"Hidden input area of electronic device" is a newly disclosed patent application, which describes the technology of using micropores to sense input. Apple The company said that the significance of the granted patent and the new patent application is to eliminate the large buttons, keys or other mechanical structures used to sense the input on the device. This is because traditional input elements may lack flexibility or adaptability and may permanently indicate the existence of input devices.
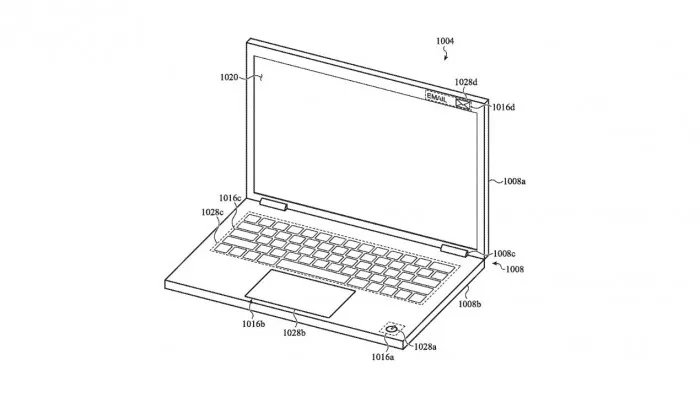
The solution is to add an input surface on the outside of the device, including a micropore array. When active, these micro perforations can display virtual keys, buttons, or notification graphics to illuminate an input area. Apple said in the patent that the input area is visually imperceptible when it is not illuminated. In other words, the goal is to make these areas invisible when not in use.
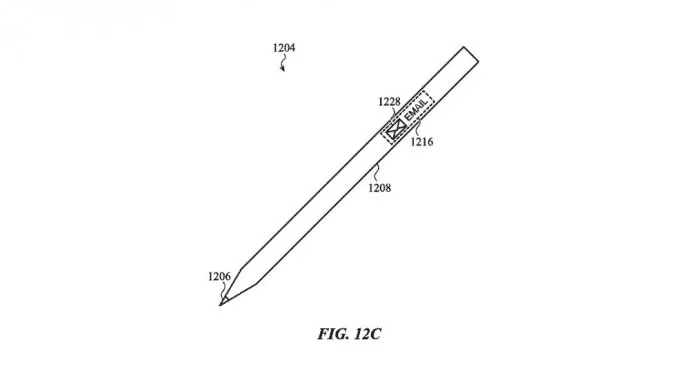
These invisible input areas can be further configured to receive input, detect touch, or use other methods, such as optical, magnetic, and capacitance based sensors, to achieve device control. Apple said it could also configure a tactile part to simulate the tactile response of a key or button. The input layer can also contain a translucent layer made of "glass, ceramic, plastic or a combination thereof". Apple said the translucent layer could be the top shell of a laptop.
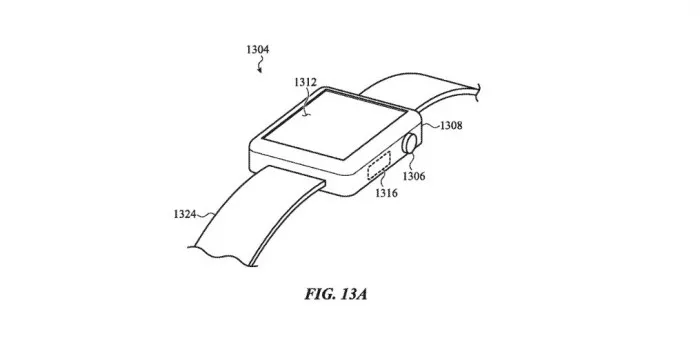
It is worth noting that this technology seems to be similar to that on homepod. Its top input area lights up when Siri is activated. Apple iPhone And iPad The device also has capacitive buttons, which, although not actually a button, can provide tactile response. Apple has obtained other patents related to microporous lighting. For example, a 2012 patent describes a system that uses similar technology to create invisible device control, which can illuminate when activated to indicate the control area.
The system can be used in combination with other apple patented technologies, such as MacBook Glass keyboard on Pro or seamless all glass iPhone.