Recently, a zero day vulnerability of Microsoft support diagnostic tool (MSDT) called "follina" surfaced. At that time, security researchers discovered the vulnerability, and due to media reports, the news has spread. Microsoft initially apparently ignored this vulnerability as a non security issue (, but later, the company admitted that it was a remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability and assigned it a trace ID cve-2022-30190.
Although Microsoft does not provide an official patch except for the steps to disable MSDT, the 0patch team has released a micro patch, which you can download from the link of its official blog post.

Following follina, another zero day threat first reported two years ago also surfaced. Like follina, this threat was obviously ignored by Microsoft because the company believed that it did not meet the "instant service requirements".
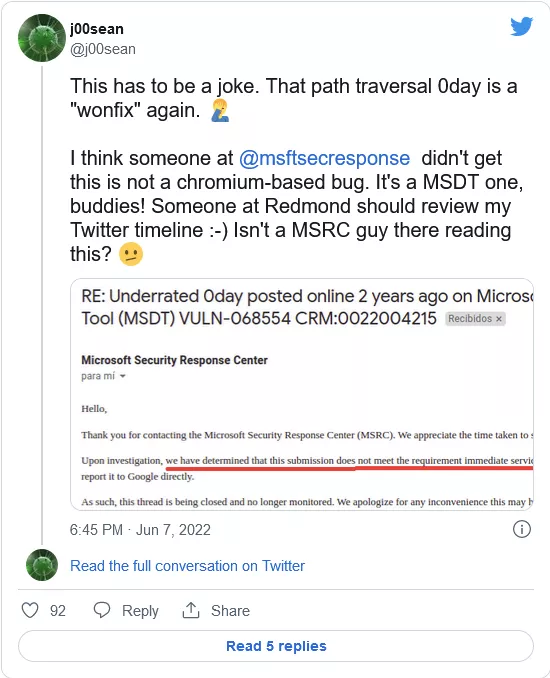
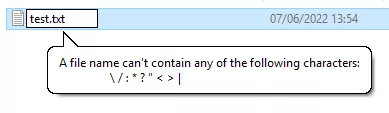
This vulnerability without tracking ID or CVE is named "dogwalk". It is found to be a path traversal vulnerability, and its payload can be placed in the Windows startup folder.
C:\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup
This means that the malware will be executed the next time a user logs on to their system. The downloaded diagcab file has a network tag (MOTW), but MSDT ignores this warning and still runs it, making users vulnerable to this potential exploitation.
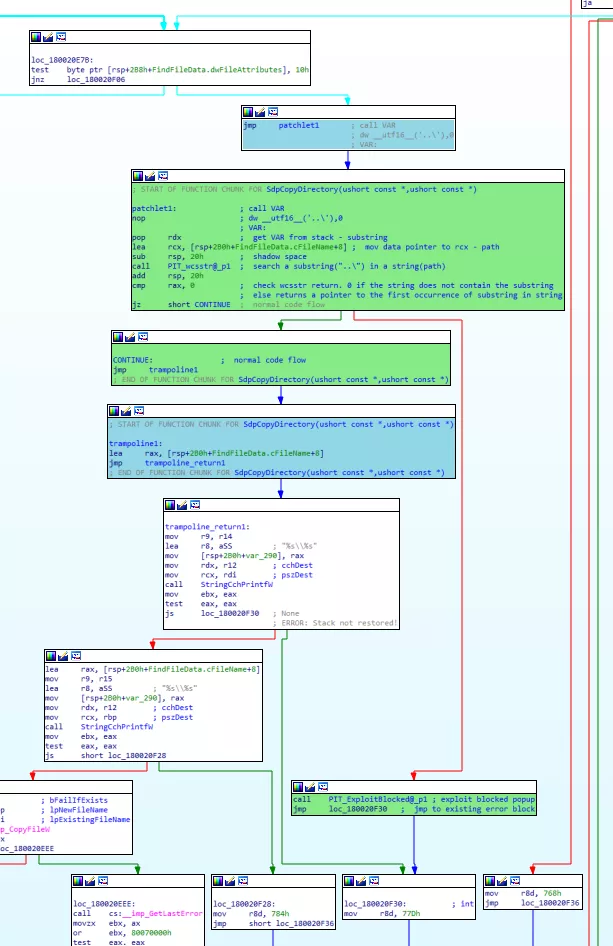
The micro patch of 0patch consists of 11 simple instructions, which can basically prevent the operation of this MSDT file. Like follina, it applies to the following Windows versions:
Windows 11 21H2
Windows 10 21H2
Windows 10 21H1
Windows 10 20H2
Windows 10 2004
Windows 10 1909
Windows 10 1903
Windows 10 1809
Windows 10 1803
Windows 7
Windows Server 2008 R2
Windows Server 2012
Windows Server 2012 R2
Windows Server 2016
Windows Server 2019
Windows Server 2022
To download the third-party patch, please go to the official blog post of 0patch linked here. You can also find more technical details in the article: