Robot clusters shuttle freely through dense bamboo forests. This scene is not from a movie blockbuster, but actually staged in Huzhou, Zhejiang Province The complex environment formed naturally is unknown to the robot without prior mapping. There is no unified central command, and each robot is "thinking independently", which depends on the on-the-spot response of the algorithm.
Dream morning comes from Aofei Temple
This research result from Zhejiang University is on the cover of the latest issue of science robotics.

According to Zhejiang University, previous robot cluster performances were mostly realized through satellite positioning and trajectory coding, which were uniformly controlled by ground computers.
In this mode, once the robot group loses its command, it will be "headless", which will not only be unable to maintain the formation, but also may hit obstacles or collide with each other.
This new achievement was evaluated by science robotics as the first cluster system capable of decentralized and autonomous flight in unstructured environment.
You can quickly return to formation after avoiding obstacles.
It can also cooperate with each other to continuously track specific targets.
So how did the team of Zhejiang University do it?
*(the complete demonstration video is at the end of the text)*
Flock pattern
This paper introduces that the research of flying robot is inspired by animals and can be divided into insect swarm mode and bird swarm mode.
Insects do short-range reactive movements (such as flies avoiding swatters).
*Response based swarm navigation algorithm * requires less computing power and memory, and robots can do less.
Birds have more sensitive senses and larger brain capacity, and can do long-term trajectory planning .
*The bird swarm navigation algorithm based on trajectory planning * has stronger performance and scalability, so the team of Zhejiang University chose this one.

In the group trajectory planning algorithm, if only spatial factors are considered, it will affect the cooperation between robot clusters. For example, when passing through a narrow space, it will be congested, causing the robot behind to have to detour.
Therefore, the team of Zhejiang University makes trajectory planning for time and space at the same time, and uses sparse parameter optimization and constraint transcription methods to improve the speed and achieve real-time calculation.
When crossing the high-density bamboo forest, this algorithm allows multiple robots to avoid collision through narrow gaps successively, without fear of inclined bamboo and undulating terrain.
In addition to trajectory planning, the team of Zhejiang University has improved the Visual inertial odometry for group positioning.
In order to avoid the small errors accumulated over a long distance and eventually cause mutual collision, a distributed drift correction algorithm is developed.
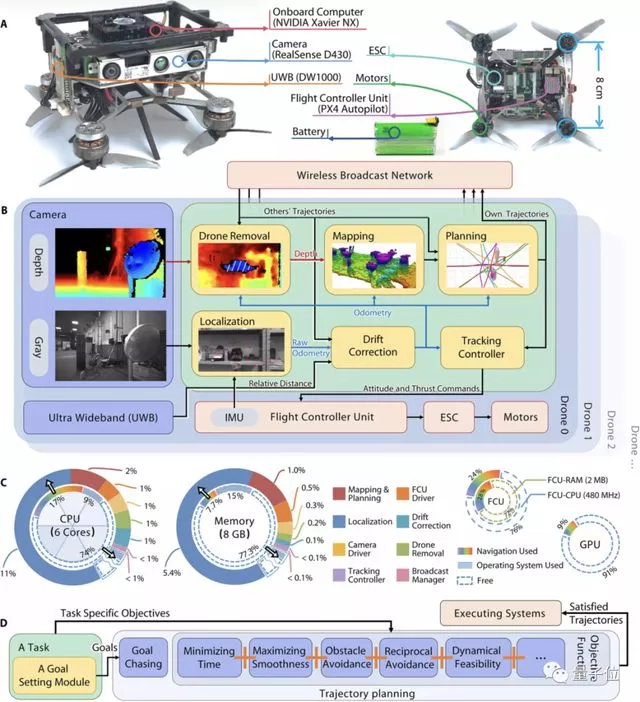
Each robot has complete sensing, positioning, planning and control functions, and uses high fidelity wireless communication to share the trajectory with each other.
In 10 robot intensive flight experiments, the researchers turned off the GPS signal, temporarily added obstacles, and human active interference without collision.
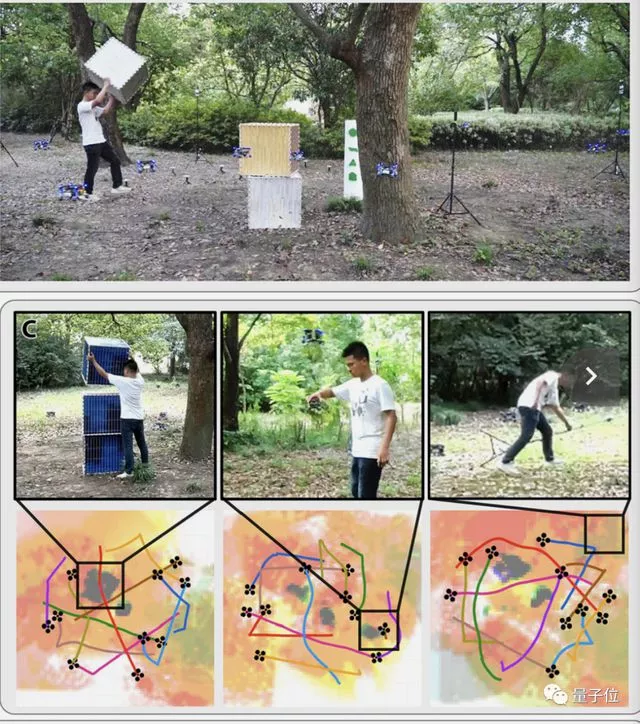

The robot used in the experiment was developed by the school of control science and engineering of Zhejiang University and Huzhou laboratory.
A single robot is only the size of a palm, which is lighter than a can of coke.

Equipped with NVIDIA Xavier NX module, it has 6-core CPU, 384 core GPU and 8GB memory.
However, in the experiment, except for some exceptional scenarios, the utilization rate of CPU and GPU remained below 40%, and the complex behavior was realized with limited computing resources.
It will be used for disaster relief, exploration and transportation
The first author of the paper is Zhou Xin , a doctoral student in the school of control science and engineering of Zhejiang University, and the corresponding authors are Dr. Gao Fei and Professor Xu Chao .
The team members are from the school of science and engineering and Huzhou Research Institute.

This achievement solves the problem of autonomous navigation of robot clusters in chaotic field environment and improves the adaptability to various practical tasks.
In earthquakes, floods and fires, robot clusters can be used to search, guide trapped people, or transport emergency supplies.
In ecological research and geological exploration, robot clusters can be used to investigate narrow environments.
The developed autonomous navigation algorithm can also be used for Mars rover, lunar rover and multiple cargo UAVs to transport goods with weight exceeding the transportation capacity of a single vehicle.



