European and American economic data are poor. The factory orders of "European locomotive" Germany in March hit the largest monthly decline since October last year, accelerating the decline of the euro. An official of the European Central Bank warned that the European economy had stalled. The number of Americans applying for unemployment benefits for the first time last week recorded 200000, higher than the expected 180000; Labor productivity fell by 7.5% in the first quarter, the fastest decline since 1947, and labor costs soared. The interest rate on the most common 30-year fixed mortgage in the United States rose to 5.27%, the highest since August 2009, suggesting that the housing market continues to cool.
The world's major central banks have entered the interest rate hike mode. The Bank of England announced its interest rate hike at its fourth meeting since December last year. The interest rate hike was 25 basis points, and the benchmark interest rate rose to 1%, the highest since 2009. However, it warned that inflation would reach 10%. Next year, the UK economy fell into recession, and there was no interest rate hike of 50 basis points, which seemed "relatively Dove". The pound fell more than 2% against the US dollar to the lowest since June 2020. Poland's central bank raised interest rates by 75 basis points, but worse than expected, and the local currency zloty plunged in the short term. Olli Rehn, a more dovish member of the European Central Bank's Management Committee and President of the Bank of Finland, hinted that the European Central Bank was increasingly inclined to raise interest rates in July and August, and completely withdraw from the negative interest rate policy in the autumn.
Led by technology, the Dow fell more than 1000 points, the S & P fell 3.6%, and the NASDAQ fell 6% and closed down 5% to its lowest level since November 2020
Investors continued to digest the information that the Fed raised interest rates by the largest margin in 22 years and immediately started to shrink the table. However, yesterday's announcement that raising interest rates by 50 basis points was in line with expectations, and the market "relief rally" triggered by temporarily excluding an interest rate increase of 75 basis points was unsustainable.
On Thursday, May 5, one day after the Federal Reserve announced the largest interest rate increase since 2000, US stocks completely erased the previous day's rise and went into the "collapse" mode. The yield of 10-year benchmark US bonds also reversed yesterday's decline and rose again above 3%, reaching a three-and-a-half-year high.
U.S. stocks fell collectively in the pre session futures stage, and the NASDAQ futures fell nearly 1%. The three major indexes then jumped short and opened low. The S & P 500 index fell 1% at the opening, the Dow fell nearly 300 points, the NASDAQ fell 1.4%, and most large technology and chip stocks fell.
The sell-off of US stocks intensified before noon Less than two hours after the opening, the Dow has released more than 1000 points, the largest decline in the market this year, and completely spit back yesterday's increase of 932 points. S & P fell more than 4% and rose 3% yesterday, the largest one-day increase since 2020. The Nasdaq, which is dominated by technology stocks, fell more than 5% and rose 3.2% yesterday. Only two components of the Nasdaq 100 rose, the largest decline in the 20 month market since September 2020.
The sell-off of US stocks expanded again one hour before the close, and the main stock indexes hit daily lows The Dow fell 1376 points or 4% at the deepest point in the session, falling below 34000 and 33000 points in a row. S & P fell 194 points, or 4.5%, and fell below 4300 and 4200 points in a row. The NASDAQ index fell 781 points or 6%, the Nasdaq 100 fell 825 points or 6.1%, and fell 13000 points. Both the Nasdaq composite index and the Nasdaq composite index hit a 52 week low. The Russell 2000 small cap index, which is dominated by value stocks, also fell by more than 100 points or 5.2%.
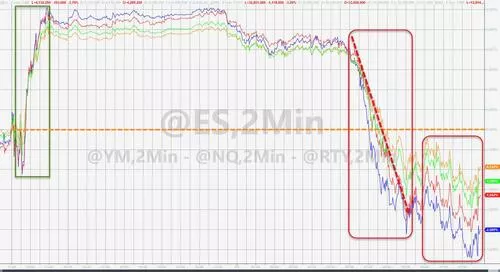
As of the closing, the S & P, Dow, NASDAQ and Nasdaq 100 all stopped rising for three days, and reported all the gains this week:
The S & P 500 index fell 153.30 points, or 3.56%, to 4146.87, the biggest decline since April 29 and the second worst single day performance of this year. All 11 sectors were wiped out, and the optional consumer sector led the decline with a decline of 5.8% dragged down by e-commerce stocks.
The Dow closed down 1063.09 points, or 3.12%, at 32997.97. The NASDAQ closed down 647.16 points, or 4.99%, at 12317.69 points, both the worst one-day performance since 2020, and the NASDAQ fell to the lowest since November 2020.
The Nasdaq 100 closed down 5.06% to a one-year low, the largest decline since September 2020, the largest intraday decline since March 2020, and a 52 week low with the NASDAQ. Russell 2000 small cap stocks fell more than 4%, approaching the lowest level since November 2020 last week.
The analysis pointed out that it seemed that US stocks did not really realize that the Fed's radical "water collection" had become the new normal until Thursday. Even if Powell temporarily ruled out the market panic of raising interest rates by 75 basis points, investors were still facing the most radical tightening of monetary policy in the United States since 2000, because Powell also hinted that interest rates could be increased by 50 basis points in each of the next two FOMC meetings. The last such significant interest rate increase was 22 years ago.
Wall Street believes that the Federal Reserve is still "open" to raising interest rates above neutral interest rates to control inflation, which finally makes the market succumb to panic, because this means that the Federal Reserve hopes to see the continued tightening of financial conditions, which will significantly crack down on high valued technology / growth stocks, and the macro economy and corporate profitability may also be affected and dragged down. Under the puzzle of "stagflation ghost", high volatility is a new market theme.
In the shadow of the hawkish Federal Reserve, many analysts suggest that stocks should be sold immediately in case of a rebound. In case the profitability of enterprises tends to be flat or decline, the existing stock market valuation will be too high. The factors that can boost the stock market in the future will either come from economic data showing that inflation has peaked, or there are signs that the economy is slowing down, and the Fed doesn't need to be so aggressive.
Zerohedge, a financial blog, noted that in the past 25 years, only two days have seen the S & P 500 index futures fall by 3% and the 10-year US bond futures fall by 1%, that is, October 9, 2008 and March 18, 2020, indicating that stocks and bonds are working together to accelerate the liquidation.
High valuation growth stocks such as star technology stocks led the decline. Yuan universe meta fell 6.8%, down from yesterday's one month high. Amazon fell 7.6% to its lowest level since early May 2020. Naifei fell 7.7%, approaching the low since the end of 2017 set last week. Apple Fell 5.6%, Microsoft and Google parent company alphabet fell more than 4.4%, Tesla fell more than 8%, both to a one week low.
Chip stocks also fell. The Philadelphia Semiconductor Index fell nearly 170 points, or 5.3%, to close down 5%, stopped rising for three consecutive days and hit its lowest level since April 29. Amd fell as much as 7.3%, down from yesterday's one month high. NVIDIA fell more than 7%, off a two-week high.
E-commerce stocks with poor financial results performed miserably, and the market was worried about the recession of "home economy" dividend. Due to the poor guidance for the second quarter, "American version Taobao" Etsy once fell nearly 19% to its lowest level since May 2020, and eBay fell nearly 12% to its lowest level since November 2020. Shopify, a one-stop SaaS e-commerce service platform in Canada, fell nearly 15% to its lowest since April 2020, with poor revenue and profitability in the first quarter. WAYFAIR, an e-commerce provider of household goods, fell by more than 25% to its lowest since April 2020, and its loss in the first quarter was greater than expected.
However, twitter bucked the trend, rising by 4.3% and closing up 2.7%, rising for two consecutive days and recovering more than half the decline since April 25. Tesla CEO musk obtained another $7.1 billion financing commitment for the acquisition of twitter, or served as Twitter's interim CEO for several months after the acquisition. However, Musk's acquisition will lead to antitrust review by the Federal Trade Commission (FTC).
While oil stocks such as Mobil and Chevron fell together, Western oil companies also rose against the market, rising by 4.8% and hitting a 52 week high, closing up more than 1%, rising for four consecutive days to the highest since mid April 2019. Regulatory documents show that Buffett holds more than 15% of his shares. On the first two days of this week, Berkshire increased its holdings of the company for the first time since mid March, buying 5.9 million shares with a total of 142 million shares.
In addition, booking holdings, the world's largest online travel service provider, once rose 5% and closed up more than 3%. Its revenue in the first quarter exceeded expectations, and it is expected that the global tourism recovery trend is strengthening in the second quarter. Sports brand lululemon fell by more than 7% to a new low in one and a half months.
Popular Chinese stocks fell along with the market. China ETF kweb fell 7%, cqqq fell 5.6% and Nasdaq Jinlong China Index (hxc) fell 7.7%. Among the four constituent stocks of Nasdaq 100, JD fell 6%, pinduoduo fell more than 11%, and Baidu and Netease fell nearly 6%. Among other stocks, Alibaba fell 6.7%, Tencent ADR fell 5.9%, station B fell 10.7%, iqiyi fell more than 13%, shell and ideal car fell more than 8%, zhongweilai, the "three fools of making cars", fell more than 15%, and Xiaopeng automobile fell more than 13%.
European stocks, which closed at midday in US stocks, were dragged down. More than 1% of the intraday gains were wiped out to the end. The pan European Stoxx 600 index closed down 0.74%, the lowest since March 15 for two consecutive days. Among them, tourism stocks fell more than 3.6%, insurance stocks fell 2.8%, but banking, technology and transportation stocks rose. The stock indexes of Germany, France and Italy all changed from rise to fall. The British stocks dominated by foreign traders closed up due to the fall of sterling, and the Russian MOEX stock index rose by more than 1.2%. Airbus, which reported good results, rose by more than 6%. The European shares of oil giant shell, whose profit in the first quarter reached a high since 2008, rose by 3%, and its US shares also rose for a time.
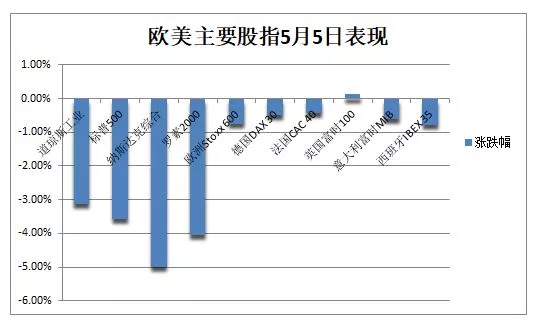
The yield of 10-year US bonds returned to above 3%, hitting a three-and-a-half-year high, and the long-term yield increased more sharply
U.S. bond yields of various maturities reversed Wednesday's decline, rose collectively on Thursday and recovered all yesterday's decline. The yield of long-term U.S. bonds increased even more, and the 5-year / 10-year yield curve ended upside down. US bond yields fell yesterday after Powell said it would not raise interest rates more aggressively.
The 10-year benchmark US bond yield rose by 19.3 basis points, breaking the daily high of 3.10%, breaking the three-and-a-half-year high since the end of 2018, and the after hours trading of US stocks was 3.03%. The yield of 30-year long-term bonds rose by 20.5 basis points, breaking the daily high of 3.20%, also a new high since 2018. The after hours trading of US stocks was 3.11%, which maintained a sharp increase of 11 basis points compared with the 10-year yield.
The two-year US bond yield, which is more sensitive to monetary policy, rose by 12.4 basis points, reaching 2.74% daily, also approaching the highest since the end of 2018, and the after hours US stock market was close to 2.70%. The five-year yield rose by more than 16 basis points to 3.06%, and US stocks fell 3% after hours.
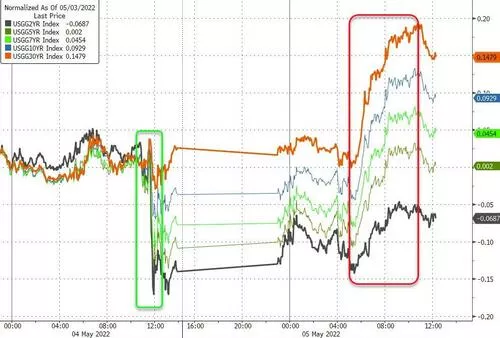
The collective rebound in US bond yields is related to the hawkish Federal Reserve, but some analysts believe that with the redistribution of global pension investors with $52 trillion in assets to almost risk-free treasury bonds, the 10-year US bond yield will peak in the 3% region.
The yield of 10-year German bonds rose 7 basis points to 1.04%, which broke the 1% mark. The yield of 10-year British bonds retreated to the trading level, temporarily reported at 1.97%. The yield on Canada's 10-year bond rose to 3%, the first time since 2011. Concerns about the impending economic recession pushed the credit risk of European junk bonds and investment grade bonds to the highest level in two years.
The dollar index hit a 20-year high of 104, the euro fell 130 points and the pound fell 200 points to its lowest level in nearly two years
The basket of dollar index DXY, which measures the dollar against six major currencies, returned to a 20-year high, rising as high as 1.3% to 103.04, breaking the high since December 2002, breaking 103 and pushing up 104 again. It fell 0.9% on Wednesday, the biggest decline since November 2020.
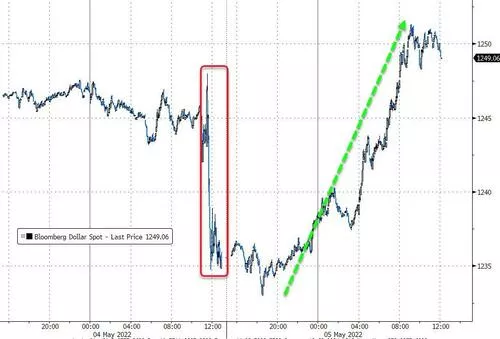
The euro once fell below 1.05 against the US dollar, falling nearly 130 points, or 1.2%, not far from the five-year low since January 2017 set on Friday. The pound fell nearly 200 points or more than 2% against the US dollar to its lowest level since June 2020, falling below the three levels of 1.26 to 1.24 in succession. The yen also fell more than 1% against the US dollar and fell below the 130 mark, not far from the 20-year low of 131 on Friday.
The analysis pointed out that the rise of the US dollar is related to the hawkish interest rate hike of the Federal Reserve and the overall risk aversion demand of the market, while the decline of sterling and euro is related to the European economy or falling into recession and the speed and range of interest rate hike are lower than that of the Federal Reserve. Some analysts believe that the US benchmark interest rate is expected to double to 1.9% in July and may double to 2.7% by the end of this year. The firm hawkish outlook distinguishes the fed from other central banks.
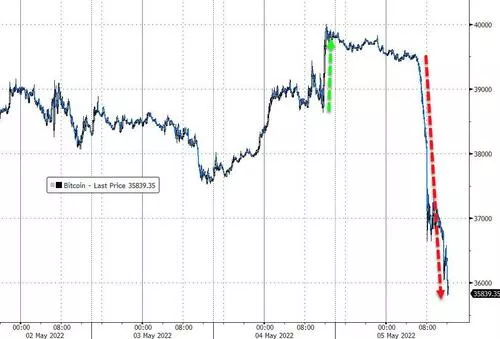
Cryptocurrencies fell as risk sentiment ebbed. Bitcoin, the largest leader in market value, fell 9% and once fell $36000, the biggest decline in nearly a month. It rose more than 6% and broke $40000 yesterday. Ethereum, the second largest by market value, also fell more than 7% and lost $2800.
OPEC + insisted on a small increase in production, and the US government will replenish inventories in the autumn. The international oil price once rose by more than 3% and remained stable at $110
WTI June crude oil futures closed up $0.45, or 0.42%, at $108.26/barrel. Brent July crude oil futures closed up $0.76, or 0.69%, at $110.90/barrel.
After the news that OPEC + insisted on a small increase in production rather than an excessive increase in production, the WTI of PetroChina rose to a daily high of US $111.34, breaking the whole figure of US $111. The highest rise in the day was US $3.53, or 3.3%. Oil distribution also rose to a daily high of $113.99, close to $114, up $3.85 or 3.5%, and then narrowed due to the ebb of risk sentiment and the strong rise of the US dollar.
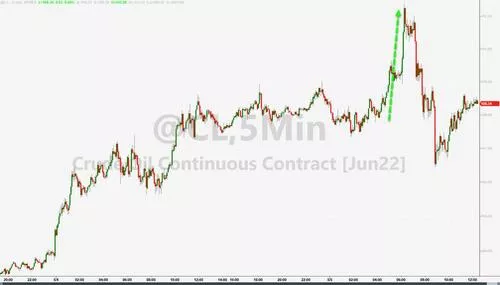
Factors boosting oil prices also include: the U.S. Department of energy today announced a long-term plan to replenish emergency oil reserves. The first batch of 60 million barrels of bidding will be held this autumn. Combined with the EU or a new round of sanctions to gradually ban the import of Russian crude oil this weekend, the market with low inventory and low idle capacity will be more tight. Analysts predict that oil prices will continue to rise in the summer.
Ice UK natural gas futures rose 4.41% to 166.23 pence / kcal, after rising to 172.500 pence. European benchmark TTF Dutch natural gas futures rose 2.6% to 106.51 euros / megawatt in late European trading, with the highest intraday rise above 111 euros. Electricity prices in Germany will rise by more than 3% in the coming month and year. NYMEX June us natural gas futures closed up 3.84% to US $8.7830/million BTU.
Under the pressure of soaring US dollar and interest rate, spot gold rose above US $1900 and then fell. Lun copper rose for two consecutive days, but less than US $9500
At the beginning of the session, the price of gold expanded due to inflation concerns, but the US dollar and US bond yields soared together, which finally weighed on the price of gold on Thursday. COMEX June gold futures closed up 0.3% to $1875.70 / ounce.
Spot gold rose by more than $28, or 1.5%, breaking the key integer of $1900 and pushing up to $1910, but US stocks fell in midday trading and returned below $1880, stopping rising for two days. Some analysts said that the new round of European sanctions against Russia increased the demand for hedging.
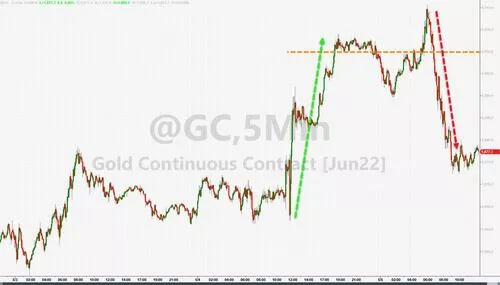
Most base metals in London ended lower, but Lun copper, which closed at less than US $10000 for several consecutive days, closed up slightly by US $16, rising for two consecutive days and still closed at less than US $9500 / ton. Lunxi stopped rising for two consecutive days and closed down $116. Lunni fell for five consecutive days, pushing down to $30000, hitting a nearly two-month low and closing down more than $500 on Thursday.
The night market of internal futures closed up and down in different ways, with methanol rising by more than 1.4% and fuel falling by more than 2.7%, leading the worst performance. Thread fell 1.34%, hot coil fell 1.50% and iron ore fell 1.04%. Among the "three brothers of coal", coke fell 0.38%, coking coal fell 1.05% and dynamic coal fell 1.69%.
