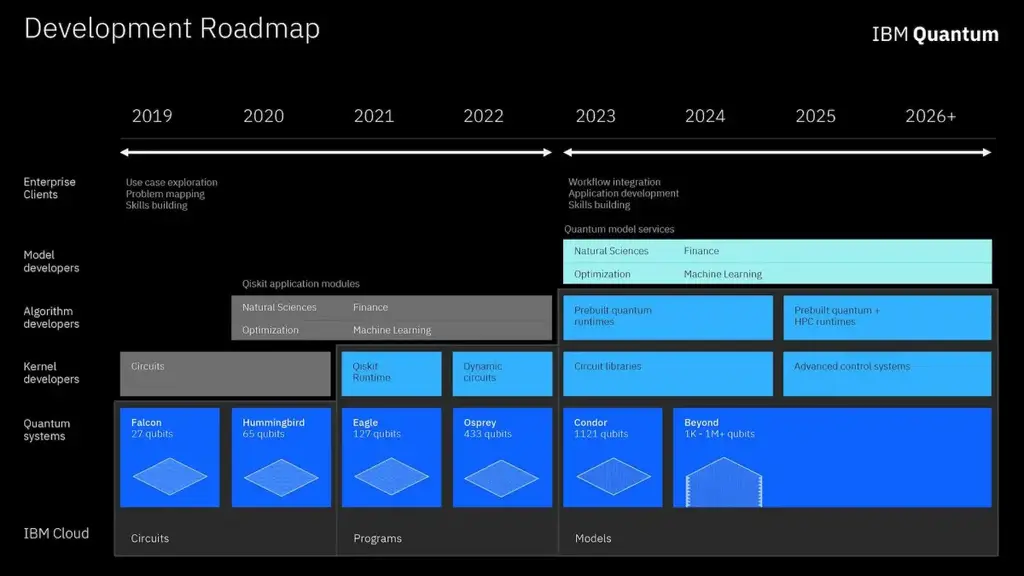
IBM today announced an upgrade to its existing quantum computing roadmap, aiming to achieve a supercomputer with more than 4000 qubits by 2025 According to the roadmap, IBM will carry out more powerful combination and coordination of classical and quantum resources to realize "quantum centered supercomputing".


IBM said it expects to provide software tools in 2023 to enable developers to work and help them make use of both quantum and classical computing resources. IBM said it believed the steady development of quantum expansion would not stagnate.
The company uses the term "serverless quantum" to describe an architecture that deploys infrastructure to allocate work to classical or quantum types of processors.
Jerry Chow, IBM researcher and director of quantum infrastructure, said: "serverless quantum is part of preparing the world for quantum centric supercomputing. He compares this effect to today's elastic computing methods. In this sense, you have the need for computing resources".
Chow said in an interview with VentureBeat that the idea is that part of the problem can be handled by classical CPU, GPU or non classical QPU, namely quantum processing unit. This is achieved by a common service layer that effectively coordinates or arranges workload distribution.
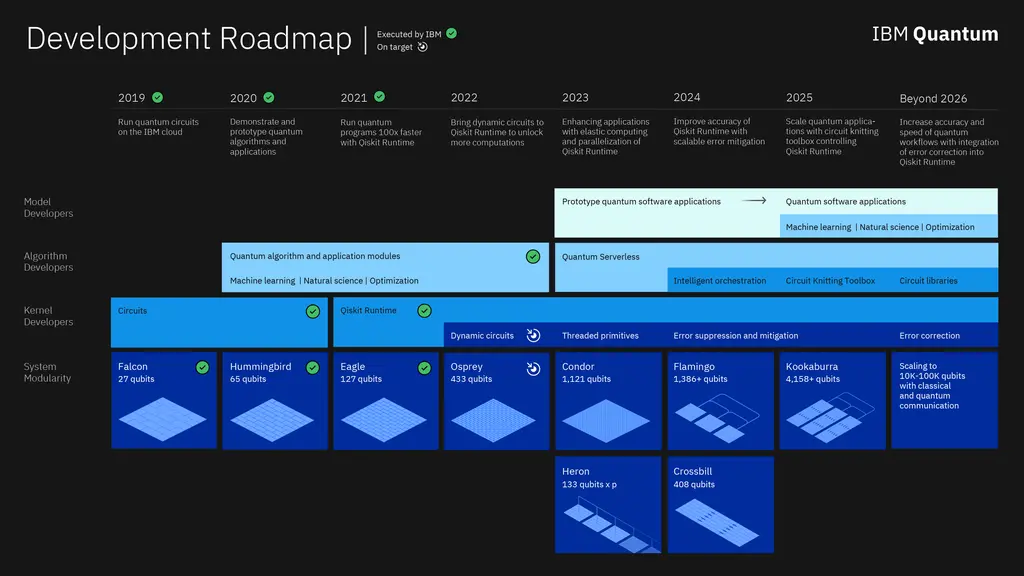
When discussing the quantum "circuit knitting" plan, it is also very important to better the hardware and software methods of inter chip communication in the process of quantum exploration.
"This is equivalent to finding a way to decompose the larger problem into small-order quantum circuits, and then weave or take all the results and reassemble them," he said. Imaginary problems are multifaceted, and some seem particularly urgent. For example, simulating nature with quantum systems is considered to be a way to improve efficiency and promote significant improvements in environment, society and governance.
IBM said that the serverless quantum function in its qiskit runtime software, including circuit weaving, will support the distribution of parallel work in 2023. In addition, the company said that improvements in error mitigation and suppression are expected to improve the quality of quantum results. These will serve qisket in 2024 and 2025 as part of the road map.
Dario Gil, President of IBM research, said: "In just two years from 2020, IBM has made great progress in the development of quantum computing. When we gradually realize our vision, we see the potential and possibility of quantum and determine the resources needed to move towards the era of practical quantum computing. With the progress of quantum serverless operation, hardware and software technology, and the theoretical objectives described in the development roadmap, IBM looks forward to creating a new era of quantum centered supercomputer Generation, providing our partners and customers with strong and abundant computing power ".
According to the quantum roadmap newly released by IBM, IBM will realize the scalability of quantum processors through three dimensions:
First, communication and parallel operations are established between multiple processors in the traditional way. The quantum processor, which integrates traditional computing resources, widens the way for more meta technologies needed to realize practical quantum systems, such as improved error suppression technology and intelligent workload scheduling ability.
Secondly, implement a scalable architecture, including the deployment of chip level short-range couplers. These couplers closely connect the chips to form a larger single processor to meet the key scalability requirements of modular quantum computing.
Third, to achieve real scalability, we must establish quantum communication between quantum processors. To this end, IBM has proposed to connect clusters into larger quantum systems.
The above three technologies for scalability will help IBM achieve the latest quantum development goal: by establishing a modular and scalable processor cluster, it will launch a system with more than 4000 qubits in 2025.