Deviant art is expanding its tool for detecting stolen encrypted art and providing it to artists outside the platform. Deviant art protection system was launched last year for works of art published on the website, and now it will also apply to works not on the website. Users can upload copies of works of art to protect and match them with unforgeable token (or NFT) images cast on several public blockchains.

If the same or nearly the same match is detected, they will receive an alert and can send a deletion request to major NFT markets such as opensea.
The new version of protect allows anyone to upload 10 pictures (no more than 2GB in total) and monitor them for free, or users can register deviant art's "core" service for $3.95 a month to monitor up to 1000 pictures, with a total of 50GB.
Protect scans the coin images on Ethereum, klaytn, polygon, arbitrum, optimization, palm, tezos and flow blockchains. If a match is detected, the artist can choose to send a pre filled Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) request to ask the market to delete the illegal NFT.
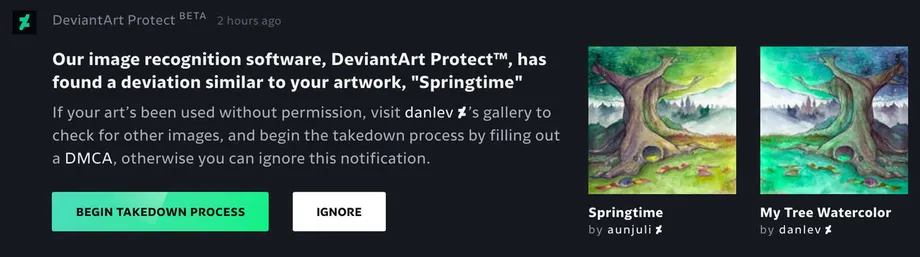
The picture shows an example of a sign of a potentially stolen artwork
Unfortunately for artists, there is no easy way to make pictures disappear from the blockchain, whether they are encoded directly into the blockchain or added to other places as a link. Deviant art CMO Liat gurwicz said: "once something is cast into the blockchain, even if it is later confirmed as infringement, it is very impossible to actually delete it from the blockchain. The copyright situation of NFT is very complex and has basically not been solved in court. Connecting encrypted tokens with works of art is not a traditional copyright infringement."
However, the NFT market usually displays images of works of art, providing the obligee with space to request cancellation. Moreover, the vast majority of NFT sales are carried out through opensea and a few other markets, which creates a major bottleneck in the so-called decentralized system. Gurwicz said: " [if ] it is not reflected in any market, it is likely that no one has seen or tried to buy the NFT."
Market platforms are increasingly interested in stolen or "copied" NFTs, which is a widely recognized problem in this field. Opensea recently launched its own system to detect imitators and scan duplicate parts of existing NFTs on the platform. However, many artists oppose adding their works to the blockchain for various reasons, including the environmental impact of the popular Ethereum blockchain.
Deviant art introduced a protection mechanism for users of the platform last September. All pictures on deviant art will be automatically monitored for three months, and the works of core users will be monitored by the system indefinitely. So far, deviant art said that it has indexed 345 million NFTs from eight blockchains and issued 245000 alerts about possible stolen works of art; It did not say how many of these triggered requests to remove the market.
Many network platforms are trying to use the function of promoting "Web3" technology based on blockchain. Instagram and twitter have special NFT image display options, and spotify is testing a way for artists to promote their digital collections. Gurwicz said deviant art is theoretically open to this prospect, but now it is clear that there is little demand for it. "I think in the past year and a half, we have understood that the greatest demand from our community is the protection of their art," she said. "So that's what we're focusing on right now." Deviant art has received a request to increase support for audio and video content, and it is also considering the option of scanning these files.
It is possible for artists to find new ways to sell the right to use their works without relying on a few centralized network platforms. But now unfortunately, Web3 has not fulfilled this promise. The creators have not been able to enjoy the opportunity, but have suffered a lot of fraud and abuse, as well as violations of their works.
The high cost of processing transactions like Ethereum will also increase the cost of purchasing NFT by tens or even hundreds of dollars - making the system infeasible for those who want to sell their works at a lower price.