With the rapid development of neural rendering technology represented by nerf, the academic community is no longer satisfied with synthesizing several new perspectives to make photos move. The next challenge is outputting 3D models directly from photos , which can be directly imported into graphic production lines such as movies, games and VR.

The photos used are either from a high-quality database or directly collected from the Internet. The equipment, weather and distance of each major scenic spot taken by tourists will be inconsistent.
The generated results have complete structure from a distance and rich details from a closer view. If you have a VR device, you can also preview the 3D version directly in the demo.
This latest breakthrough was jointly completed by the teams of Zhejiang University and Cornell University, and was listed in the graphics summit siggraph 2022**.

Before that, 3D models generated by similar technologies could not even have complete shapes.
Seeing this, netizens have expressed that the progress in this field is faster than people think.
Slow down and wait for me.
So, what did this research rely on to make a breakthrough
Fusion of two sampling methods
Specifically, the basic framework of this study draws lessons from neus on neurips 2021, a method that combines implicit neural standards with volume rendering.

However, neus uses the sphere based sampling method, which is suitable for close range and small objects.
For large buildings with complex structures, a large number of sampling points will be collected in the blank area, which will increase a lot of unnecessary calculation pressure.
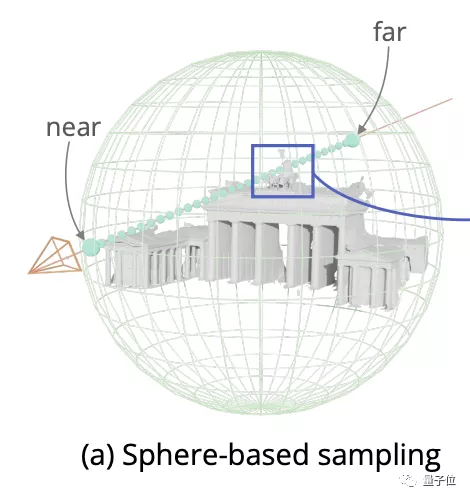
To solve this problem, researchers have proposed voxel guided and surface guided (surface -A new sampling method of mixed.
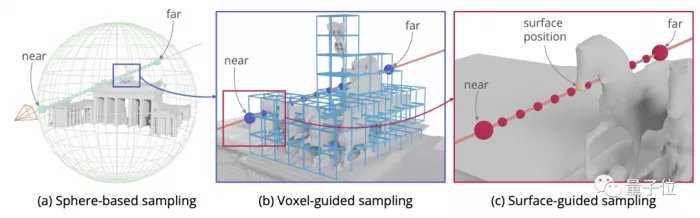
Voxel guidance can avoid unnecessary waste, and the training ray can be reduced by 30%*.
Combined with surface guidance, the sampling density around the real surface is increased to help the neural network better fit and avoid losing details.
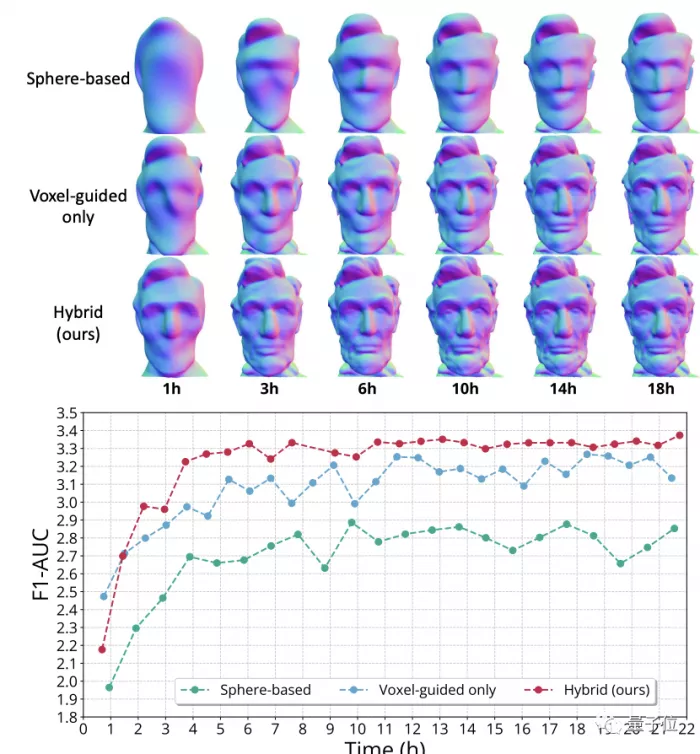
In the ablation experiment, it can be seen that the voxel guided method converges faster than the sphere based method, but it is not as detailed as the hybrid method.
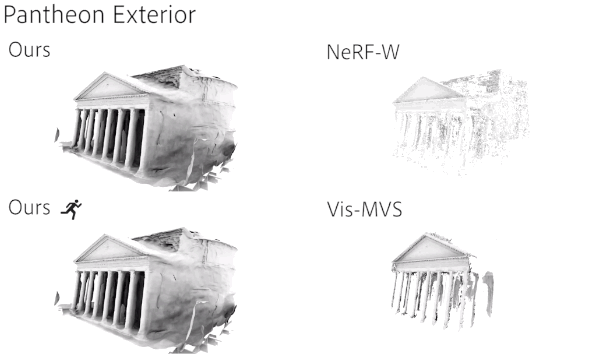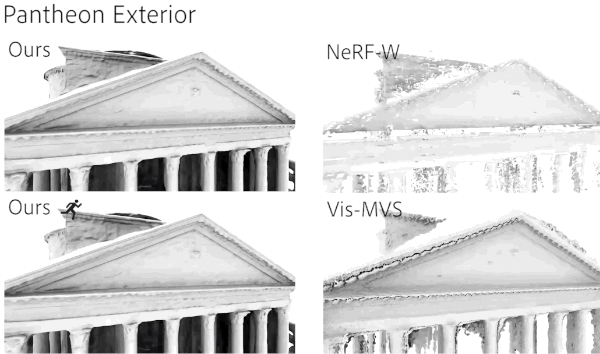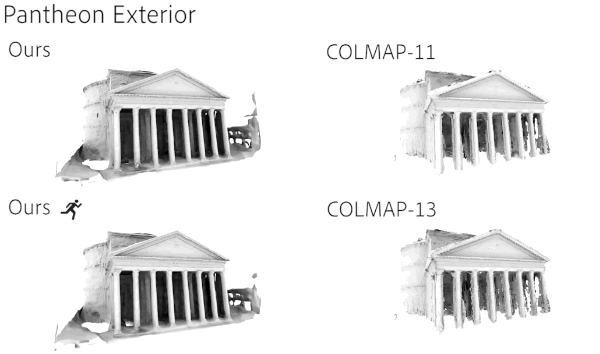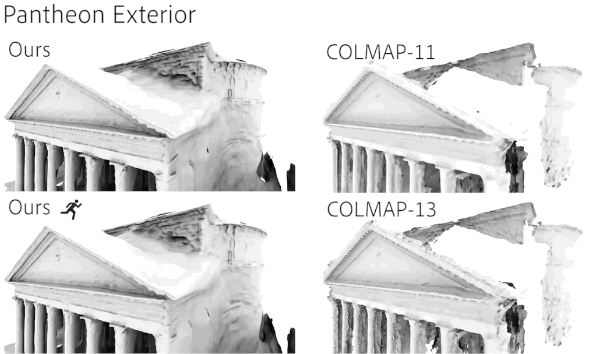
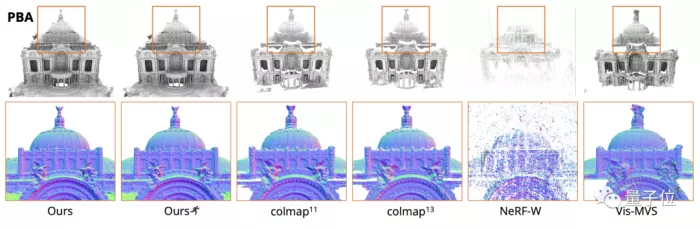
Compared with previous similar studies, the integrity and details of the model generated by the new method are better.
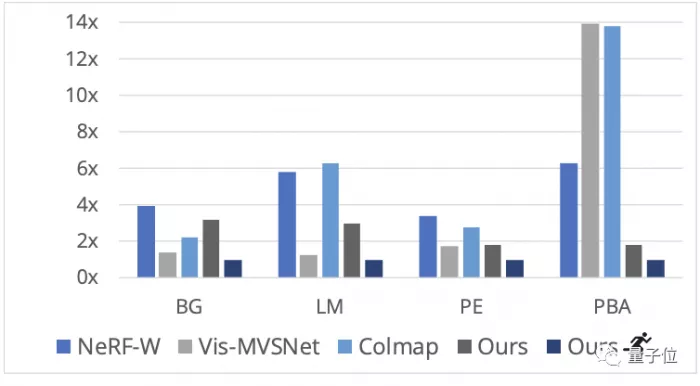
The training speed also has obvious advantages, especially in the large-scale scene Mexico City Art Palace (PBA).
△
Ours is the result of complete convergence, and the one with the villain icon is a checkpoint in the training process
Of course, the new method is not completely flawless.
One limitation inherited from nerf is that the final result will be affected if there is deviation in camera position calibration.
Another problem that is difficult to solve is that the back and interior of buildings that cannot be photographed cannot be accurately reconstructed.

One More Thing
Finally, I would like to add that some members of the Zhejiang University team have previously studied neural 3D human reconstruction.

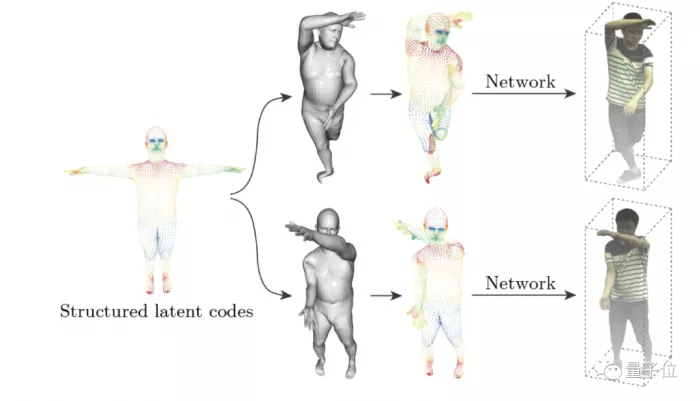
It can be applied to video playback that provides a free perspective for sports competitions.
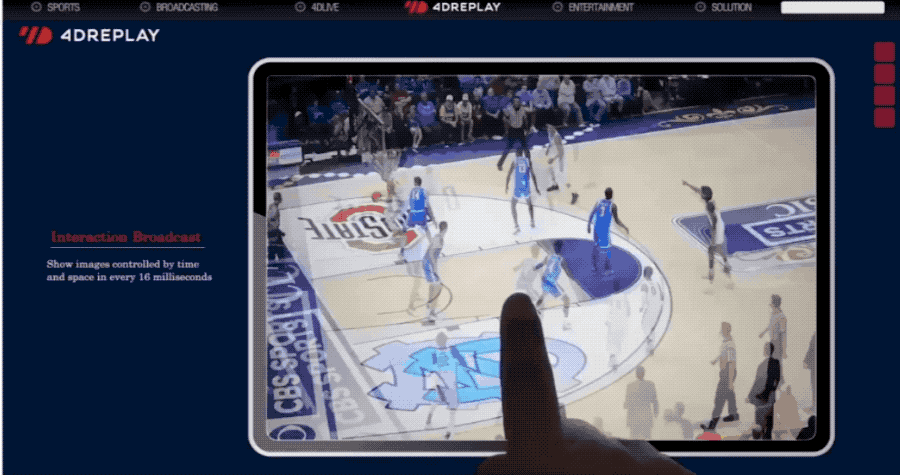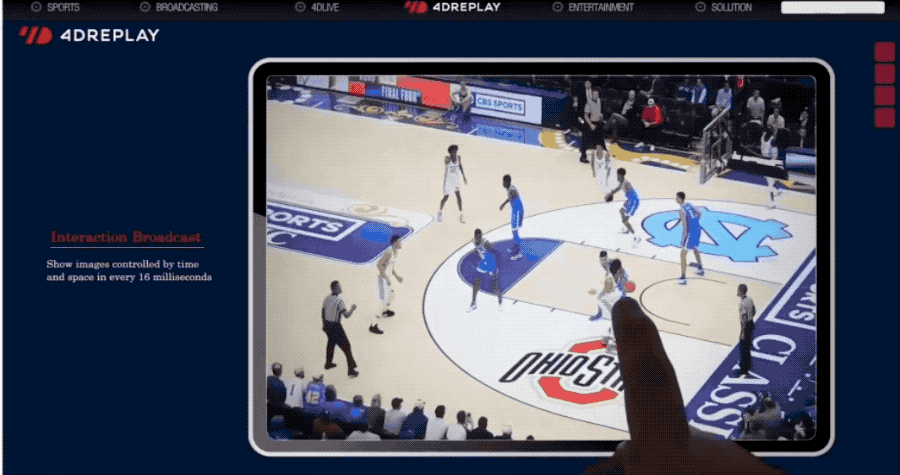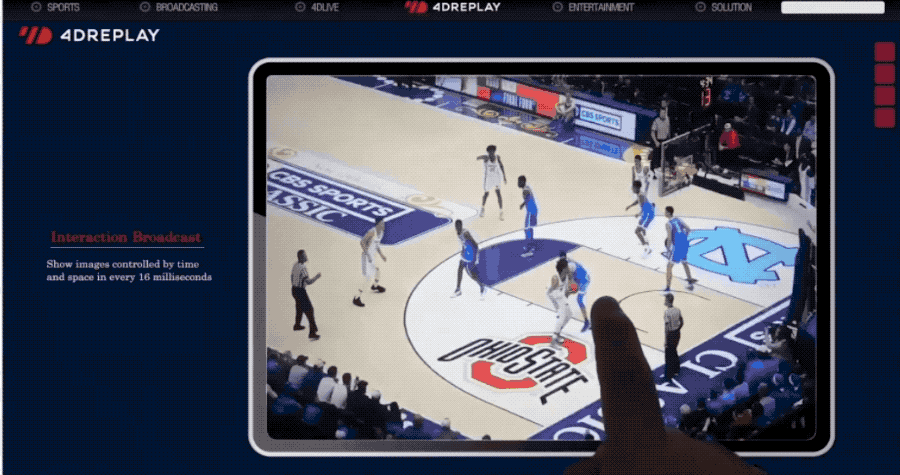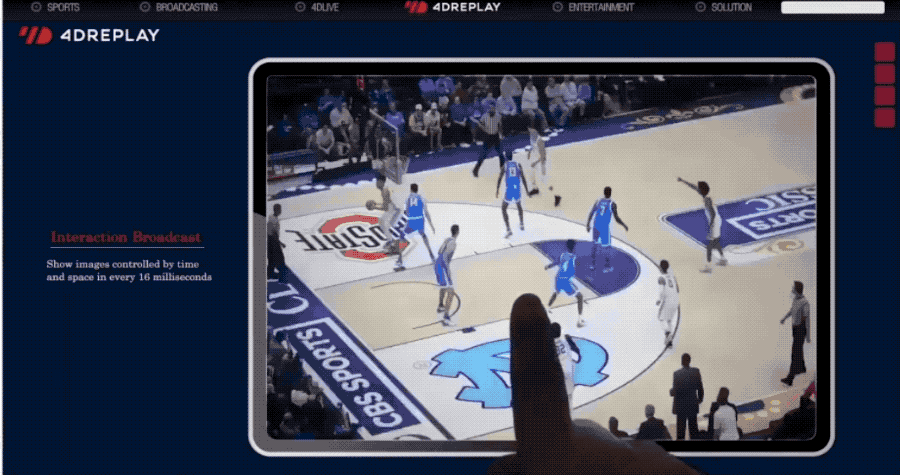
It's also 666.