The space launch system (SLS) is a super heavy expendable launch vehicle that NASA has been developing since 2011. It will be able to launch heavy payloads into orbit and provide a basis for human exploration beyond Earth orbit. SLS is designed to be evolvable, so it can support many types of tasks in the future. These larger and more powerful SLS versions will require larger and more powerful boosters.
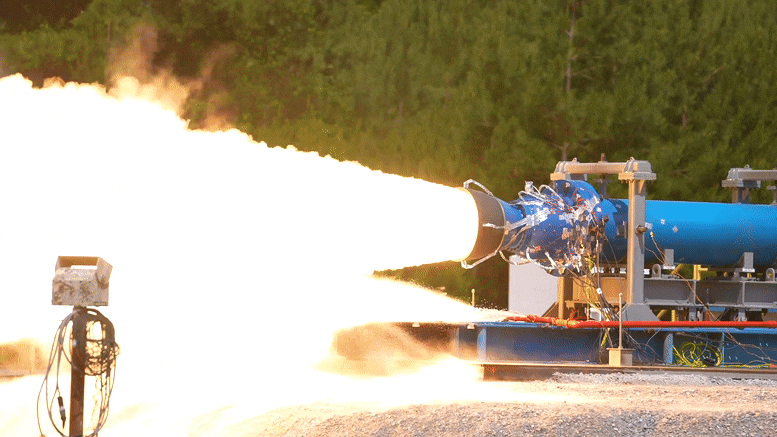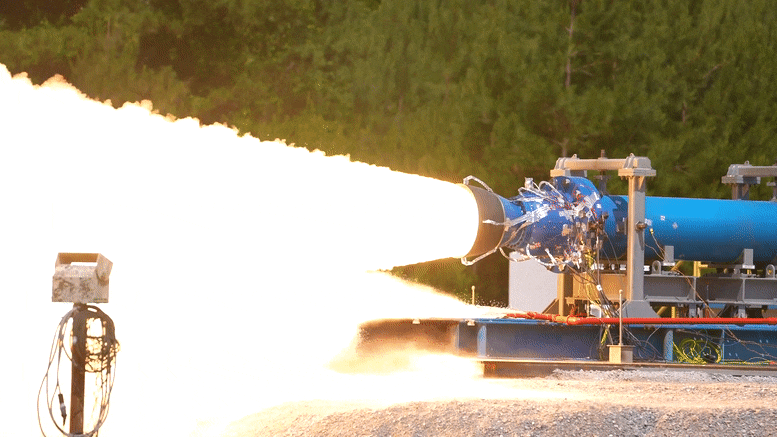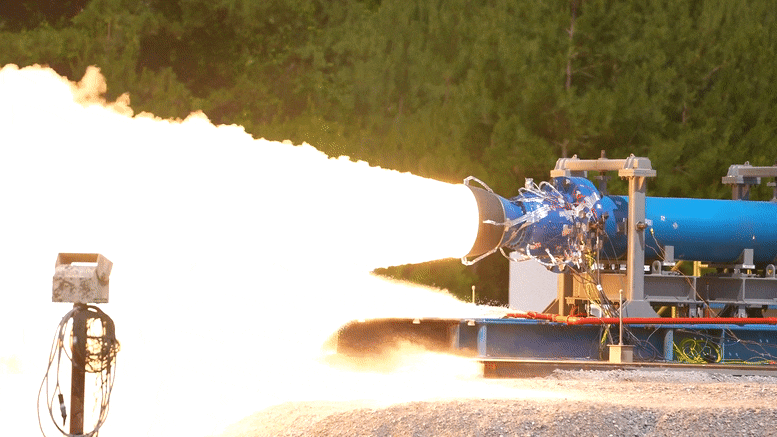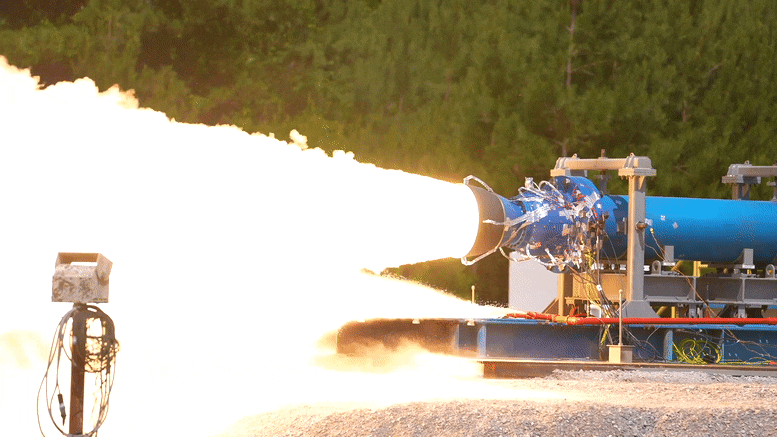
As part of the development of this upgraded booster, engineers successfully launched a 2-foot diameter subscale solid rocket booster at NASA Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama on June 1 local time.
It is reported that the test was conducted in the East test area of Marshall and generated 92000 pounds of thrust. As part of the booster obsolescence and life extension (Bole) plan, it will provide upgraded booster design for the evolution configuration of Artemis IX and future space launch system rockets. The bole booster will be a larger and more powerful solid rocket motor that will enable SLS rockets to deliver heavier payloads to the moon and elsewhere.
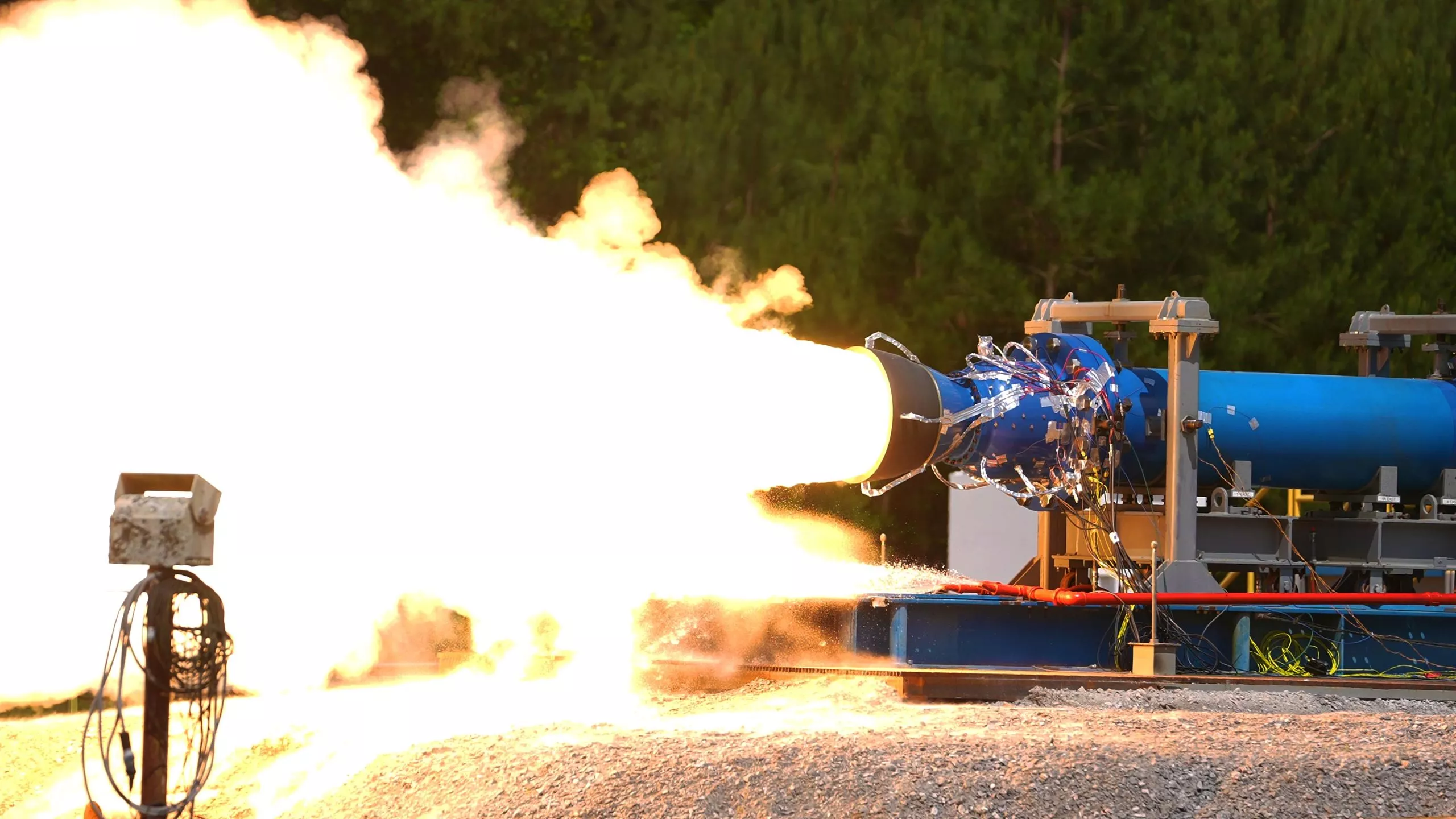

It is understood that this test is the second test of this series. The purpose is to evaluate the new engine design, in which a half section, a new propellant, a new rear dome design and a new nozzle design are added. The first test was completed on December 2 last year, when 76400 pounds of thrust was generated.
In this second test, Northrop Grumman, the chief booster contractor, used a different propellant from the first test, which put the engine under the maximum expected working pressure that may be experienced on the launch day. Engineers will use the test data to analyze the performance of the engine under this pressure, which may reach a very hot day on the launch pad of NASA Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
The third scale test of the new design planned to be carried out next year will evaluate the alternative materials of the motor nozzle and insulation materials. Sub scale engine test is an important step to understand the performance of Bole engine in full scale. The team is working to complete the final design for full-scale motor testing at Northrop Grumman's test facility in Utah in the spring of 2024.