The study found that adults aged 18 to 44 with pre diabetes were more likely to be hospitalized for a heart attack than those without diabetes. A heart attack occurs when the flow of blood to the heart is greatly reduced or blocked. This blockage of the heart arteries is usually caused by the accumulation of fat, cholesterol and other substances.
The most common cause of heart attack is coronary artery disease. A strong spasm or sudden contraction of the coronary artery may cut off the blood supply to the myocardium, which is a less common cause.
Risk factors for heart attack include hypertension, hyperlipidemia and smoking. Recent studies have also found that high blood sugar may also increase the risk of heart disease.
According to the preliminary study presented at the 2022 American Heart Association Scientific Conference on nursing quality and results, young adults with blood glucose levels higher than normal (indicating pre diabetes) are more likely to be hospitalized for heart attack than their peers with normal blood glucose levels. The academic exchange was held in Reston, Virginia, from May 13 to 14, 2022. It included the latest research on cardiovascular medical quality and patient outcomes for the treatment and prevention of heart disease and stroke.
Pre diabetes means that a person's blood glucose level is higher than usual. The fasting blood glucose level is between 100 and 125 mg / dl, but it is not high enough to be diagnosed as type 2 diabetes. Pre diabetes symptoms are widespread, which can increase the chances of developing type 2 diabetes. According to the data of the National Institutes of health, more than 88million people aged 18 and over in the United States have pre diabetes, accounting for more than one third of the national adults, of which pre diabetes affects about 29million people aged 18 to 44.
Author of the research report Akhil Jain, M.D., a resident at Mercy Catholic Medical Center in Darby, Pennsylvania, said: "If pre diabetes is not treated, it will seriously affect health and may develop into type 2 diabetes. It is well known that this will increase a person's risk of cardiovascular disease. As heart attacks are increasingly occurring in young people, our research focus is to identify the risk factors related to this young group, so that future scientific guidelines and health policies can better address the cardiovascular problems related to pre diabetes Disease risk. "
The researchers reviewed the patient health records in the national inpatient sample, which is the largest public inpatient database in the United States. Specifically, they studied the inpatient records related to heart attacks among young adults aged 18 to 44 in 2018.
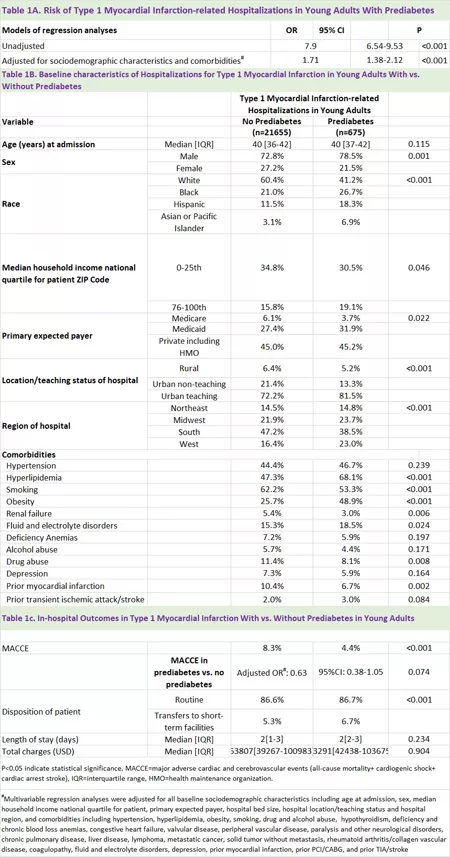
The analysis found that:
Among the more than 7.8 million young adults hospitalized in 2018, there were more than 31000, or 0.4%, and the blood glucose level was related to pre diabetes.
Among people with pre diabetes, the incidence of heart attack was 2.15%, while that of young adults with normal blood glucose levels was 0.3%.
Adults with pre diabetes were more likely to have high cholesterol (68.1% and 47.3%, respectively) and obesity (48.9% and 25.7%, respectively) than their peers without pre diabetes.
Adults with pre diabetes who are hospitalized for a heart attack are more likely to be black, Hispanic, or Asian / Pacific Islander racial or ethnic men.
Compared with heart disease patients without diabetes precursor, adults with diabetes precursor who are hospitalized due to heart attack are more likely to have higher family income, be hospitalized in urban teaching hospitals or in the Midwest and western regions of the United States.
After taking into account various influences and correction factors, the researchers found that young adults with pre diabetes were 1.7 times more likely to be hospitalized for a heart attack than their peers without pre diabetes. Despite a higher risk of heart attack, young people with pre diabetes did not have a higher incidence of other major adverse cardiovascular events, such as cardiac arrest or stroke.
Although pre diabetes is a precursor of type 2 diabetes and other serious health complications, it can be reversed. Many of the steps taken to prevent pre diabetes are the same as those taken to prevent heart disease.
"When the blood glucose level reaches the standard of pre diabetes, it gives us an alarm to take action." Eduardo Sanchez, MD, master of public health, faha Faafp said: "For patients with pre diabetes, knowing that lifestyle change is the key to improve their blood glucose level and overall health, and may reverse pre diabetes and prevent type 2 diabetes. Healthy diet and active body, if necessary, weight loss are meaningful ways to reverse the diagnosis of pre diabetes. For smokers, it is also very important to participate in the smoking cessation program. Other lifestyle and behavior changes, such as reducing stress Forces may seem small, but they can have a great impact on many different areas of life and can also bring change.
The in-depth study of heart attack in young adults with pre diabetes seems to be quite scarce, and more work needs to be done. Since nearly one-third of adults in the United States have pre diabetes, researchers should be regarded as the basis for future research to clearly determine the heart disease burden of young adults with pre diabetes. It is necessary to raise young adults' awareness of the importance of routine health examination (including pre diabetes screening), and take measures to prevent or delay the development of type 2 diabetes and related cardiovascular events (such as heart attack).