After six years of efforts, Italian and Austrian researchers have creatively developed a three in one hybrid material, which is called the new generation of "smart skin" Its sensitivity is 1000 times that of real skin. It can detect touch, temperature, moisture and even microorganisms, which helps promote the research and development of sensitive robots and intelligent prosthetics. The related research was published in the recent journal advanced materials technology.
The intelligent skin, developed by the team of the Institute of solid state physics of Graz University of technology under the leadership of the latest research leader, Italian scientist Anna Cockett, has 2000 independent sensors per square millimeter, which is more sensitive than human fingertips. Inside each sensor is an intelligent polymer in the form of hydrogel, and the shell is piezoelectric zinc oxide.
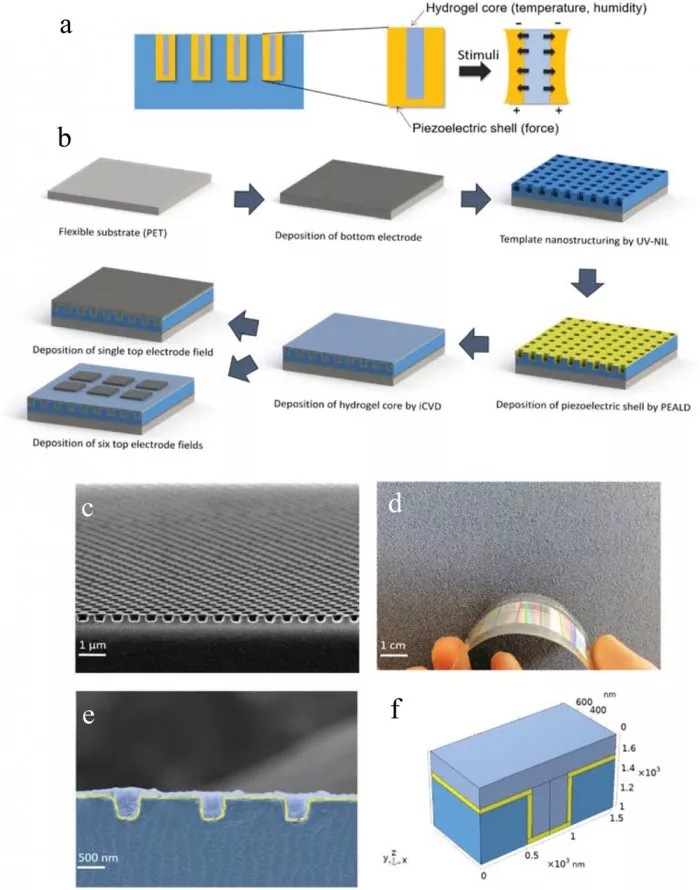
Cockett explained: "Hydrogels can absorb moisture and expand when humidity and temperature change. In this process, hydrogels exert pressure on piezoelectric zinc oxide, which responds to this pressure and all other mechanical stresses through electrical signals. This ultra-thin material can respond to force, moisture and temperature at the same time with extremely high spatial resolution and send corresponding electronic signals. This material with multi-sensor characteristics is an intelligent artificial material technology The 'Holy Grail' of the art field. "
It is reported that the thickness of the first batch of artificial skin samples is 6 microns, while the thickness of human epidermis is 0.03-2 mm. Artificial skin can also be made thinner. In addition, human skin can perceive objects about 1 mm2 in size. The sensitivity of artificial intelligent skin is 1000 times that of human skin, and it can detect smaller objects such as microorganisms.
The researchers said that for the first time, they combined three physical and chemical methods: chemical vapor deposition of hydrogel materials, atomic layer deposition of zinc oxide and nano printing lithography of polymer templates to develop this smart skin. Intelligent skin is expected to be applied in many fields. For example, in the field of medical care, it can independently detect microorganisms and give relevant reports. It can also be used for human prostheses that can sense temperature or humidity, robots that can more sensitively sense the environment, etc.
The core components of the smart skin are produced by steam based manufacturing process, which is now very mature, so the smart skin is easy to expand. The research team is currently optimizing the characteristics of the skin, hoping to expand the temperature range of the material reaction and improve its flexibility.
[chief editor's circle]
Human beings' expectations for robots are not limited to making them talk and move. This is only "local" intelligence. If they have smell, touch, perception and even thinking like human beings, they will be one step closer to real intelligence and more in line with our understanding of intelligence. The intelligent skin developed in this research is one of the ways to make robots more intelligent. It is worth mentioning that this kind of intelligent skin is more sensitive and powerful than human skin, giving full play to the great advantages of intelligent sensing.