The researchers found that the thermal properties of energy storage equipment have undergone key changes during operation, paving the way for better thermal management Modern energy storage devices, such as supercapacitors and batteries, have highly temperature dependent performance. If a device becomes too hot, it is prone to "thermal runaway".
"Thermal runaway" - or uncontrolled overheating - can eventually lead to dangerous explosions or fires. In order to make the equipment operate stably and safely, it is necessary to adopt a wise thermal management strategy. To do this, it is necessary to understand how some thermal characteristics, such as heat capacity, change dynamically during charging and discharging.
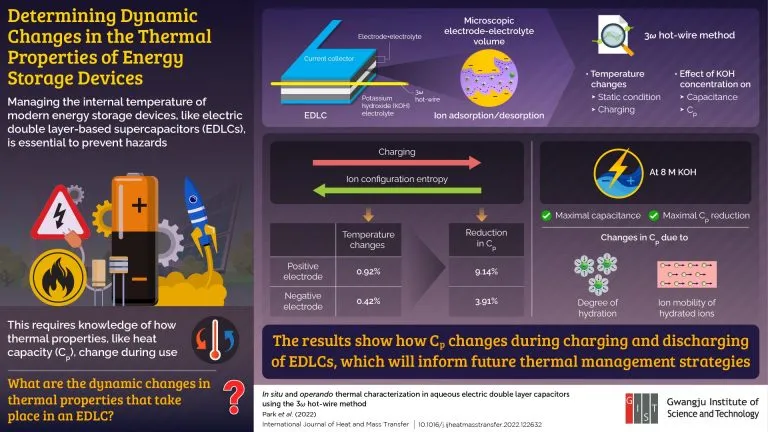
Recently, researchers from Gwangju University of science and Technology (GIST) in South Korea investigated the thermal characteristics of electric double layer capacitor (EDLC) - a super capacitor with high power and long life, which laid a technical foundation for thermal measurement and revealed important information. Professor Jae Hun SEOL, who led the study, explained: "use 3 ω With the hot wire method, we can measure the heat capacity change of EDLCs in real time in the micro electrode electrolyte volume, which is an active place for ion adsorption and desorption. "
The study was published online on February 5, 2022 and will be published in the [International Journal of heat transfer] on June 1, 2022( https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0017931022001144?via%3Dihub ) 》Vol. 188, No. 122632.
The research team conducted experiments in situ (under static conditions) and operation (during charging). They found that during charging, the temperature of the positive and negative electrodes changed by 0.92% and 0.42% respectively, which corresponds to the reduction of their respective heat capacity by 9.14% and 3.91%. "According to thermodynamic theory, the ion configuration entropy (a measure of randomness) of the system decreases during adsorption, that is, charging. This also affects the free energy of the system. Professor SEOL explained:" this together leads to the decrease of heat capacity. "
The team also changed the concentration of electrolyte potassium hydroxide to see how it affected the performance of EDLC. They found that EDLC showed the greatest reduction in capacitance and heat capacity when the electrolyte concentration was 8m. They attributed this to changes in the degree of hydration of ions and their ion mobility.
"An important aspect of this study is that charging and discharging also change the heat capacity of EDLC," Professor SEOL said. "These findings will expand our understanding of the basic Thermophysics of EDLCs."
In fact, these results can be considered as an important step towards an effective thermal management strategy in the future, which will create safer and more reliable energy storage equipment.