The Physical Activity Guidelines recommends that adults aged 18-64 years need to perform muscle strength exercises at least twice a week, in addition to 150-300 minutes of moderate intensity or 75-150 minutes of high intensity aerobic exercise per week.
What is muscle strength training? Why are muscle strength exercises recommended for the average person? And how should the average person perform muscle strength exercises?
What is muscle strength training?
Muscle strength training, which is what we often hear as resistance training, is also called resistance training.
Muscles are like a "rope" that is fixed to the bones at either end of the joint by tendons. When the muscle contracts, a force is generated and the end of the 'rope' pulls the bones around the joint towards the fixed end of the 'rope', thus creating joint movement.
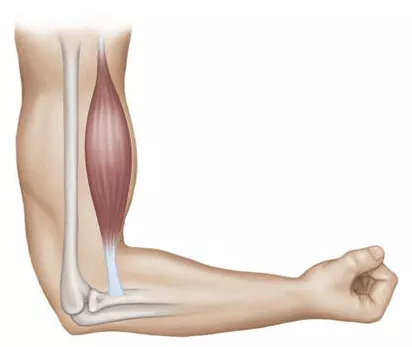
Essentials of Strength Training and Conditioning in In everyday life, the bones at one end of a rope are often also subject to resistance from external objects. For example, if we pick up a heavy object, the weight acts its own gravity on the bones, which we call resistance 'FR'. Muscle contraction produces muscle force, which acts on the bones at the other end along the muscle fibers and tendons "FM". At this point the joint is like a hinge, the centre of the joint is the fulcrum, one end is muscle force and one end is resistance, their vertical distance from the fulcrum is the muscle force arm 'MM' and the resistance arm 'MR'.
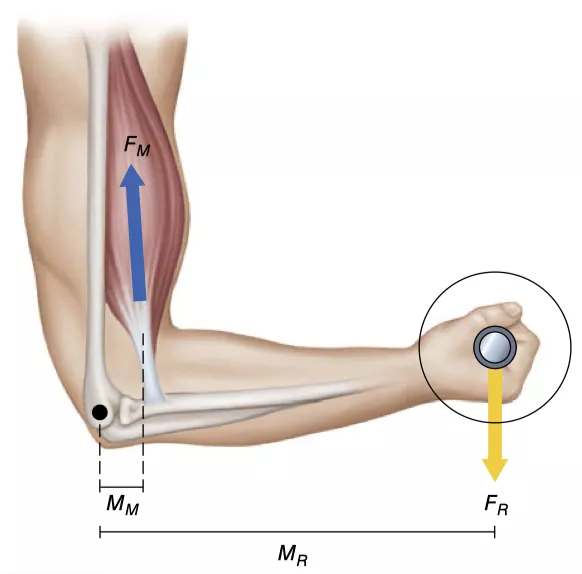
Essentials of Strength Training and Conditioning When " Muscle Force x Force Arm" > "Resistance x Force Arm", i.e. FM x MM > FR x FR, the muscle shortens and the joint rotates in the direction of the muscle force, at which point it is called a centripetal contraction action.
When "muscle force x force arm" = "resistance x force arm", i.e. FM x MM = FR x FR, the muscle length will remain constant and the joint will remain fixed, which is called an isometric contraction.
When "muscle force x force arm" < "resistance x force arm", i.e. FM x MM < FR x FR, the muscle is elongated and the joint moves in the direction of resistance, which is called a centrifugal contraction action.
All of the above processes of muscles firing against resistance to produce movement are called resistance exercises, and the training we do specifically for resistance exercises is called resistance training.
Classification of resistance training
Depending on the source of resistance
Resistance training can be divided into self-weight training and weight training depending on the source of the resistance.
self weight training
Self-weight training, or training with one's own body weight, is the basic way to operate resistance training. This type of training uses the individual's own weight as a source of resistance. For example, push-ups, pull-ups, sit-ups, etc., street fitness is typical of self weight training. In addition, gymnastics and yoga are also categorized as self weight training.
A common problem with self weight training is that the resistance load is limited by the individual's body weight, preventing further increases in the load and thus limiting the development of one's absolute strength.
Another problem with self weight training is the inability to apply the right load for the individual; for example, if someone is not strong enough to perform pull-ups at all, he will not be able to perform the exercise effectively, and although other movements can be substituted, they are still limited in terms of load regulation.

Image from the web
Weight training
Weight training refers to resistance training using various tools to apply weight. Two common forms are "stationary equipment training" and "free weight" training.
Fixed apparatus training refers to resistance training for specific muscle groups performed on apparatus that provides adequate stability and is ideal for novices. It is important to note that during stationary equipment training, the activation and power of the stabilizing muscle groups are inadequate, which is detrimental to the migration of training results. For example, if someone has poor lower-body stability, the ability of the lower-body muscles to maintain stability will not necessarily increase through stationary equipment training, although his lower-body strength will increase.
Free weight training is resistance training that uses free objects to provide resistance. Free weight objects are not attached to anything and can be picked up and moved at the discretion of the trainer. Commonly used tools such as barbells, dumbbells, kettlebells, etc., and common movements such as barbell squats and dumbbell squats. Free weight training requires the trainer to keep their body stable during resistance and is therefore more difficult compared to stationary equipment training. For example, the barbell squat is harder than the Smith squat, so less weight can be squatted.

Image from the web
Depending on the purpose of the training
Depending on the purpose of the training resistance training can be divided into muscle maximal strength training, muscle explosive training, muscle hypertrophy training, muscle endurance training and stability training. Different training objectives can be achieved by adjusting the load, number of repetitions, and interval time between sets of resistance training.
Muscle Max Strength Training
Maximal strength is the force produced by the muscles and muscle groups in a single maximum effort while maintaining proper posture, and to put it simply, it is the maximum force your muscles can produce. Because muscles move slower when producing maximal force, maximal force is also called slow plyometric force. Maximum strength is usually measured by the amount of weight that can only be completed once in a movement, also called 1RM, for example, if a person bench presses, and when weighted to 100kg he can only complete it once with all his strength, the 1RM of his bench press is 100kg.
Muscular maximal strength training is resistance training with maximal strength as the main goal, and bodybuilding competitions and Hercules competitions are events that primarily measure maximal muscle strength.

Image from the web
explosive muscle training
Explosive muscle power, the ability of muscle tissue to contract rapidly to produce force, requires muscles to produce maximum power output in short, fast movements, primarily as a function of the anaerobic functional system, hence the names fast muscle power and anaerobic power. Explosive power can also be measured by the 1RM in explosive movements such as the high roll, the 1RM in the snatch, or by the height of the vertical vertical jump. The height of our jumps depends on the explosive power of the lower body muscles.
Explosive muscle training is resistance training with explosive power as the main goal, and the weightlifting events in the Olympics are typical of explosive muscle power.

Image from the web
muscle hypertrophy training
Muscle hypertrophy is an increase in the cross-sectional area of muscle. Muscle fibers can only thicken and increase in cross-sectional area during resistance training adaptations, they do not increase the number of muscle fibers. Muscle cross-sectional area and strength are positively correlated, so a person with large fast muscles also has relatively greater strength. Resistance training with the main purpose of muscle hypertrophy is muscle hypertrophy training, bodybuilding and fitness programs are typical muscle hypertrophy programs, and the main training purpose of most fitness people is also muscle hypertrophy, to make the muscles fuller.
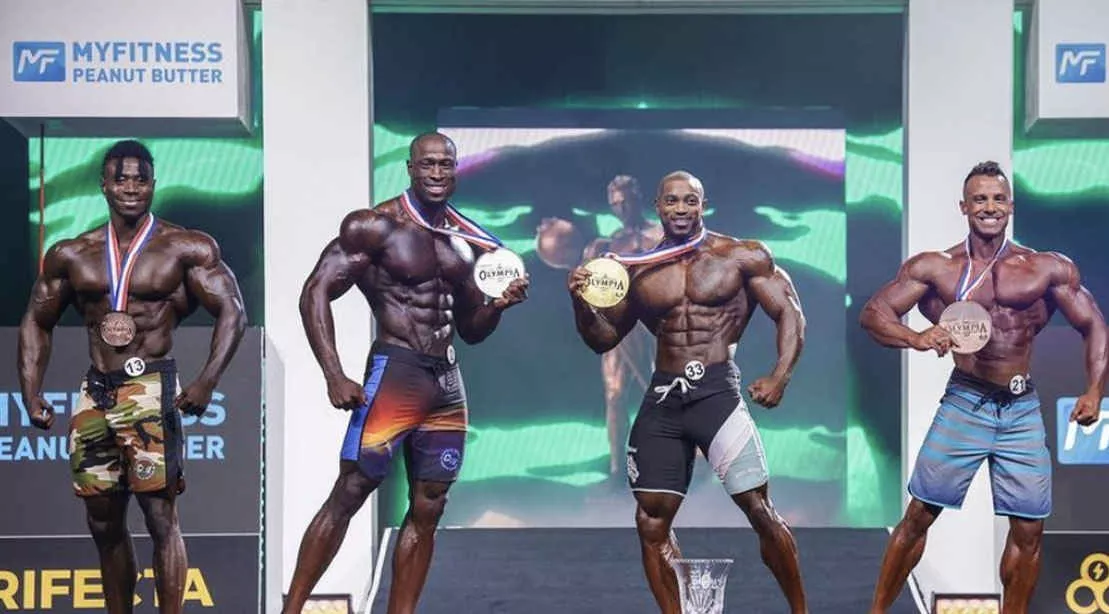

Image from the web
Muscular Endurance Training
Muscular endurance is the ability of a specific muscle to repeatedly resist non-maximal resistance, simply the ability to repeat the same movement and weight, or the ability of a muscle to maintain the same position, e.g. plank support is abdominal muscle endurance training. It is usually measured by the maximum number of repetitions of the same movement with the same load, such as the push-up test, sit-up test, and pull-up test.
Muscular endurance training is resistance training with muscular endurance as the main goal, and CrossFit training is a training system that focuses on muscular endurance.

Image from the web
Stability Training
Stability is the ability to provide optimal joint support during movement to maintain correct posture. In other words, stability is the activation of the right muscles at the right time with the right size force, in the right plane of motion. Often training in a controlled unstable environment can improve stability, such as dumbbell bench presses on yoga, which can increase joint stability. Stability is closely related to the small muscle groups around the joints.

Image from the web
Summary
There are many different types of resistance training, no matter what type of resistance training can bring great benefits to the body, but the lack of proper understanding of resistance training among the general public has led to resistance training becoming a sport for athletes and a small group of enthusiasts, so the following will focus on the benefits of resistance training and lead you to a proper understanding of resistance training.
Why does the average person need resistance training?
Resistance training has always been active in the public eye, and the developed internet allows us to look up various methods of resistance training anytime and anywhere, but resistance training is still the carnival of a small group of people, and has never been popularized on a large scale. The reason for this is that the public lacks a proper understanding of resistance training and misinterprets it as a boring exercise that only makes muscles bigger, while ignoring the importance of resistance training to health.
Resistance training is the elixir to fight aging
Muscle strength and bone mass are involuntarily lost with age. Muscle mass decreases by about 3-8% every 10 years after age 30, and declines more rapidly after age 60. Bone content is also lost gradually with age, resulting in weaker bones and increased risk of hip, wrist, and spine fractures. Loss of muscle strength and bone mass is an underlying cause and contributor to the loss of work capacity in older adults, not only increasing the risk of falls and injuries, but also potentially increasing the incidence of type 2 diabetes, obesity, and heart disease.
Neuromotor function declines as we age. Muscle strength, explosive power, reaction time, balance, and the ability to maintain postural stability all decline with age, thereby increasing the risk of falls in older individuals, bringing health, psychological, and financial losses. In particular, falls can be painful, cause fractures, and even result in disability.
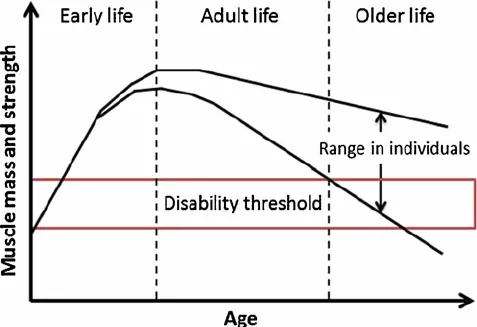
Image from the web: changes in muscle mass and strength with age and resistance training can significantly improve muscle mass, muscle strength, bone density in older adults and neuromotor function, reducing the risk of injury.
Aging does not reduce the effectiveness of the skeletal muscular system in adapting to resistance training, so with progressive resistance training, the musculoskeletal capacity of older adults can be improved, thereby reducing the risk of injury. A review study that included 23,407 adults aged 60 years showed a 34% reduction in falls among those who participated in a comprehensive exercise program that included balance exercises, resistance, and functional training.
Resistance training can also improve brain health in older adults.
People who engage in resistance training may have better brain health, and resistance training classes can stop cognitive decline due to aging. Several studies of older adults have shown that participation in resistance training significantly improves cognitive brain function (e.g., processing speed, memory, and executive function). Researchers have suggested that resistance training has neuroprotective effects, such as improved blood flow, reduced inflammation and increased expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factors, all of which are associated with memory and learning.
In addition to this, resistance training can improve a number of degenerative body functions associated with aging to combat the effects of aging.
It is worth noting that although both aerobic and resistance training are beneficial for middle-aged and elderly people, only resistance training can increase muscle strength and muscle mass. And nowadays, the vast majority of Chinese middle-aged and elderly people only perform aerobic exercises (jogging, swimming, square dancing) and neglect resistance training, which seriously affects their health and quality of life.

Image from the web
Resistance training doesn't just make you look more attractive
Resistance training can significantly improve muscle mass and compensate for physical appearance deficiencies
Most people start resistance training because they want to make their body more attractive; guys are looking for broad shoulders, big pecs, and symmetrical abs, and girls are looking for full hips and a slim waist and stomach. If you are naturally narrow shouldered, or have flat hips, you can compensate for that with resistance training. But I don't think that should be the only purpose of resistance training, we need to focus on and understand the other benefits of resistance training more.
Adding resistance training to your daily routine can reduce the risk of injury
Resistance training helps improve the toughness of ligaments and tendons, improve joint range of motion and mobility, thus building strength around major joints such as the knees, hips and ankles to provide additional protection against injury.8 More importantly, resistance training can help correct muscle imbalances, for example, having stronger core, hamstrings and glutes can reduce the load on the lower back during weight bearing (heavy lifting) and Reducing the risk of lower back injury. Studies have also found that athletes who perform regular resistance training are less likely to be injured.
Resistance training can improve your mobility and flexibility
Contrary to popular belief, resistance training doesn't make you an awkward 'goofy big guy', it makes you more flexible. Resistance training increases joint range of motion (ROM), allowing for greater mobility and flexibility. And people with weaker muscles tend to have lower ROM and flexibility. In addition, a recent review study found that stretching and resistance training were equally effective in increasing joint range of motion (ROM). It is important to note that to use resistance training to increase joint range of motion, you need to perform complete, full, movements that involve the entire joint movement, such as squatting lower and lifting higher without injury.
Resistance training can help you control your blood sugar levels
Resistance training can reduce the risk of developing diabetes and can help those with diabetes to better manage their blood sugar levels. Skeletal muscle improves insulin sensitivity and also lowers blood sugar levels by absorbing glucose from the blood and delivering it to muscle cells. Therefore, greater muscle mass can help improve the management of blood sugar. Resistance training may also reduce the risk of developing diabetes. A 10-year study involving 35,754 women showed that women who engaged in resistance training had a 30 percent lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes than women who did not engage in resistance training.
Resistance training can improve heart health
Several studies have shown that regular resistance training exercises are effective in lowering blood pressure, lowering total and LDL cholesterol (bad cholesterol), and improving circulation by strengthening heart and blood vessel function. In addition resistance training to control blood sugar levels is also beneficial for heart disease.

Image from the web
Resistance training doesn't just make you look thin it also makes you easier to lose weight
Resistance training can make you look slimmer
After regular resistance training, muscle mass will increase and body fat will drop. While you may not lose weight or even gain, it will make you look slimmer. This is because muscle tissue is more dense than fat tissue, and the same weight of muscle takes up less space on your body compared to fat. Therefore, even if you don't see a change in the number on the scale, your waist and leg circumference have already been significantly reduced.
At the same time, resistance training can significantly reduce abdominal fat. The fat stored around the abdomen, especially visceral fat, not only affects the appearance, but is also associated with an increased risk of chronic diseases (heart disease, fatty liver disease, type 2 diabetes).
Resistance training will increase your body's basal metabolism, allowing you to burn more calories
Resistance training boosts metabolism in two ways. First, muscle is more metabolically efficient than fat mass, and muscle will burn more calories at rest. Second, studies have shown that metabolic rates increase to last 72 hours after a resistance training workout. This means that extra calories are still being burned hours and even days after the workout. So if you have more muscle, you can manage to eat more food and still not gain weight and get a 'leaner body'.
Image from the web
Resistance training for a better life
Resistance training can greatly increase an individual's self-confidence
Resistance training can help you overcome challenges, work toward your goals, and appreciate your own strength. In particular, resistance training can increase your sense of self-efficacy (the belief that you can succeed or perform a task), which can greatly increase your confidence. A review study of 10-16 year olds observed a significant association between resistance training and high self-esteem, physical strength and physical self-worth. In addition, a review evaluation of 754 adults showed a significant association between strength training and positive body imagery.
Resistance training can improve your mood
Regular resistance training can improve your mood and improve your mental health. Several studies have shown that resistance training can reduce anxiety and improve mood. Resistance training offers a variety of benefits for mood regulation, such as increased self-esteem and self-efficacy. What's more, exercise promotes mood boosts the release of endorphins, which play an important role in positive emotions.
Resistance training can lead to a better quality of life
Many studies have linked resistance training to increased health-related quality of life. Quality of life is defined as the degree to which a person is physically and mentally healthy. A review of 16 studies covering adults 50 years and older showed a significant correlation between resistance training and better mental health, physical function, pain management, and overall health vitality.

Image from the web
A few suggestions for resistance training for the general population
When we learn about resistance training we realize that it has a lot of benefits, so how do you start resistance training as an average person? Here are a few suggestions for you.
Mastering the correct basic movements
If it is your first time to contact resistance training, the first thing you need to do is to learn the correct movement pattern (the sequence of each joint movement, the direction of movement, etc.), we can use the Internet to search for videos or graphic content to learn, try to find some knowledge background or training background of the shareholder to learn, but also can follow the exercises on various training APP, such as Kepp can be through the library of movements You can learn many resistance training movements on Kepp.
We recommend that you start with self-weighted resistance training movements such as push-ups, self-weighted squats, and pull-ups, progressively increasing in difficulty, such as from kneeling push-ups to standard push-ups, and from deep squats against the wall to self-weighted squats.
In addition, stationary equipment training is also great for newbies because the trajectory is fixed while providing solid support, but it needs to be offered at a specific venue.
However, both self-weighted resistance training and stationary equipment training have limitations compared to free weight training, and free weight training is also more difficult, so free weights are suitable as an advanced form of resistance training for novices.
Focus on stability training
Stability is the ability to provide optimal joint support during movement to maintain correct posture. Joint stability is closely related to the small muscle groups surrounding the joint, for example, the stability of the shoulder joint is closely related to the rotator cuff muscle group. Overall body stability is related to the strength and strength endurance of core muscle groups, such as lumbar and abdominal strength which are extremely important for body stability.
NASM (National Academy of Sports Medicine) sees stability as the foundation in resistance training, believing that only after building a foundation of stability can we make rapid progress in strength, explosive power, and muscle hypertrophy to get rid of injuries.
In traditional martial arts, movements that exercise stability such as the horse stance are treated as basic skills. When the horse stance is firmly established and stability is well practiced, the subsequent practice of other martial arts movements can only be smooth, so stability is extremely important in all kinds of training.
The author neglected stability training at the beginning of his own resistance training and blindly increased the load, which later led to problems such as muscle imbalance, joint instability, and even several injuries, and frequent obstacles to progress in muscle hypertrophy, muscle strength, and explosive power. So from personal experience is also highly recommended to develop stability first.
The training method for developing stability is outlined as practicing in a controlled instability environment. For example, we can do push-ups on a yoga ball instead of flat push-ups, and performing push-ups on a yoga ball will increase the stability of the stabilizing muscles of the shoulders and trunk by giving them a higher level of activation. Other methods such as replacing double-legged movements with single-legged movements increase instability.
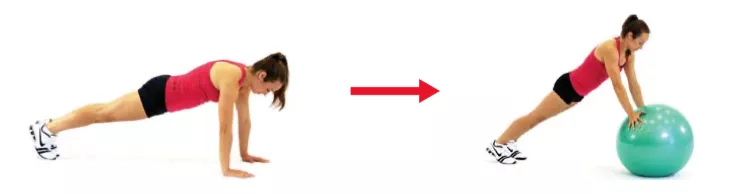
NASM-CPT National Academy of Sports Medicine Personal Trainer Certification Guide
Attention to warm-up and relaxation
A "warm-up" is usually performed before resistance training to raise muscle and core temperature, improve nerve function, reduce connective tissue adhesions, and also prevent sports injuries.
The warm-up consists of two parts, a general warm-up and a specific warm-up.
- A general warm-up usually consists of 5 minutes of low-intensity cardio, such as jogging, jumping rope, cycling, in addition to some stretching to increase joint mobility, especially for older adults, and recommended before resistance training. Stretching during the warm-up phase focuses on muscles that are tight in daily life.
- Special warm-up movements are usually similar to formal resistance training movements, e.g. to perform a deep squat exercise, a special warm-up would be to do some half-squat walks, half-squat side slides, etc., which will activate the target muscle groups and get into training shape faster.

Image from the web
"Relaxation" is generally performed after resistance training to allow the body to quickly transition to a quiet state, lower the heart rate respiratory rate and relax muscles back to an optimal state of tension and also to relieve delayed muscle soreness.
Relaxation generally consists of minimum intensity aerobic exercise, self-fascial relaxation and static stretching. Aerobic exercise lasting 5-10 minutes is appropriate, self-fascial relaxation can be performed for 30 seconds on each trained muscle using a tool such as a foam axial fascia ball, and static stretching is also performed for 30 seconds on each trained muscle.

Image from the web
Do not over train
NASM (National Association for Strength and Conditioning) recommends that novice trainers perform 2-3 resistance training sessions per week, i.e. 2-3 days between each resistance session, so that the body is sufficiently recovered to be fully engaged for the next session.
Each training time should not be too long, usually choose 3-5 movements, each movement 3-5 sets can be, training time is too long, the body can not be timely energy replenishment, training effect will also be affected.
Which should I choose, cardio or resistance training?
Aerobic exercise refers to exercise in which the body's aerobic energy supply system dominates, mainly some long duration, low intensity exercise, such as running, swimming, rope skipping, the recent good "Liu Weihong exercise" also belongs to aerobic exercise.
Whereas the body's anaerobic energy supply system dominates when resistance training is performed, resistance training is anaerobic and anaerobic exercises are mainly exercises of short duration and high intensity.
Note that duration here refers to the duration of continuous exercise. Going to the gym for 30 minutes of resistance training is not considered aerobic exercise because the duration of a single exercise session lasts only 30 seconds, while the rest period is up to 2 minutes. Rest and exercise are alternated, so resistance training is anaerobic based on the duration of the single exercise session. Running for 30 minutes is aerobic because it is a continuous exercise process with no rest or intervals in between.
Image from the web
Based on the different characteristics of aerobic and resistance exercise, they produce different adaptations to the body. The adaptations produced by aerobic training on the body are mainly in the cardiovascular as well as the respiratory system, which enhances heart function and lung function. Also, because aerobic exercise lasts longer, it is effective in burning fat and increasing caloric expenditure, thus reducing body fat.
But aerobic training is limited in terms of skeletal and muscular gains and is far inferior to resistance training. Resistance training for skeletal and muscle gains is based primarily on its overload characteristics. In resistance training we use a load that exceeds the load of our daily activities (walking, running, stairs, etc.) and therefore the bones and muscles adapt quickly under overload, with increased bone density tougher bones, increased muscle mass and thus more strength. With resistance training we are more resilient when faced with special situations. For example, if we are about to fall, we can use our strong core to re-stabilize our body, or use our upper body strength to hold on to the ground, or grab onto objects around us, thus avoiding more dangerous situations, while our tougher bones are better able to withstand greater impact and will not break easily.
Especially for people who are losing weight, while cardio is the most effective way to lose fat, resistance training is even more important to stay in shape and prevent weight regain. Because only resistance training can significantly increase muscle strength and muscle mass, as mentioned above, muscle is more metabolically efficient than fat mass, and muscle will burn more calories at rest, so when you have more muscle mass, you are less likely to gain weight and cause weight rebound even if you stop exercising temporarily. On the other hand, prolonged aerobic exercise will consume protein and break down muscle, thus reducing energy metabolism at rest, so there are many people who have been successful in slimming down through a lot of aerobic exercise and will experience rapid weight rebound after stopping exercise.
Therefore aerobic training and resistance training we can't do just one, but both to give our body all-round health. That's why the Physical Activity Guidelines for Chinese People (2021) recommends that adults need to do muscle strength exercises at least twice a week in addition to moderate or high intensity aerobic exercise.
Summary
Resistance training has always been active in the public eye, and the developed internet allows us to look up various resistance training methods anytime and anywhere, but resistance training is still the carnival of a small group of people, and has never been popularized on a large scale. The reason for this is that the public lacks a proper understanding of resistance training, and misunderstands it as a boring exercise that can only make muscles bigger quickly, while ignoring the importance of resistance training to health.
And when we learn about resistance training, we realize that resistance training leads to a great body is just one of its many benefits. Not only does resistance training fight aging and keep us safe from disease and sports injuries, but more importantly resistance training improves our quality of life and allows us to enjoy our lives more.
On the other hand, based on the different characteristics of aerobic and resistance exercise, they produce different adaptations to the body, so we need to do both in order to give our bodies overall health.
The article also gives some advice for newcomers to resistance training, such as starting with simple movements, getting the movements right, paying attention to steady development, etc. A "Resistance Training Advanced Guide" will also follow to introduce resistance training in further depth.