
Wi-Fi, on the other hand, uses 802.11 as a standard, specifying Wi-Fi generation names that are easier for consumers to understand. Generally, the larger the generation number, the greater the channel width and the higher the theoretical network speed.
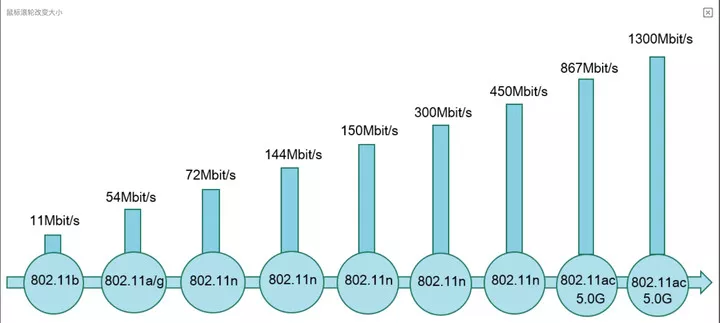
▲ Wi-Fi Rate Map
Although Wi-Fi is wireless, it has the same hardware requirements as wired networks. For 100-gigabit Wi-Fi, you need a gigabit optical cat, a gigabit WAN port, a high protocol wireless terminal card, and a Category 5 or higher network cable.

From the hardware to the protocol, from the network package to the use of terminal, direct comparison of wired and wireless network speed there are too many variables, it is difficult to rigorously answer, after all, wired and wireless network, can not be done under the same conditions of comparison. So the answer to the question of who is faster and who is slower in wired and wireless networks is not focused on speed, but on stability.
Even if all hardware and software settings are correct, Wi-Fi can still be unstable due to blocking around the router, 2.4G/5G signal interference, etc. There are so many factors that affect the speed of wireless networks compared to wired networks.
How do I make my wireless network faster?
Wireless network, wireless network, 'wireless' is its biggest advantage, and in life, like mobile phones, tablets, smart home and other devices, there is almost no way to use wired network, a host of laptops, and most of the elimination of wireless network port. Since we can't give up, it becomes a matter of concern to "make Wi-Fi as fast as possible".

If all settings are fine, but Wi-Fi is still unstable, you can troubleshoot by following these steps in addition to replacing hardware and upgrading network services.
- Environmental shading should be taken care of
When there are objects blocking around the router or wireless antenna, it is easy to cause attenuation of the wireless signal. The walls, doors, windows and glass of the room have a certain degree of influence on the signal, especially metal objects, which are likely to completely block and reflect off the propagation of the wireless signal.
When placing your router, try to remove any surrounding obstructions or sources of interference, such as walls, metal objects, microwave ovens, etc.

- Be aware that someone may be using your Wi-Fi secretly
It could be that your Wi-Fi password is too simple, it could be that some app has shared your Wi-Fi out, and unbeknownst to you, your Wi-Fi, long ago, wasn't just for you.
If you find that the network is slow, it probably has nothing to do with your settings and is just a neighbor trying to be friendly with you in that way. Change the Wi-Fi password and the network problem is solved.

- The almighty reboot that still works
Long time use will make the router generate a lot of cache, reboot can release the cache, recycle resources, also can reduce some unknown causes of system bugs, cooling lag. Most mainstream models have a built-in scheduled reboot feature, which you can adjust in the router's settings page.
In addition to these simple methods above, you can also try changing the Wi-Fi channel, or buying a signal booster to meet the network needs of multiple rooms. Sub routers, power cats, etc. are also good options.
Of course, this will require a bit of expertise or hardware upgrades, so if you're interested, search the web for keywords for details.
The settings are fine, the environment is not obscured, the reboot is done, but the Wi-Fi is still slow, then you should contact the operator. Broadband network is an extremely complex end-to-end system, we can solve the problems of the client, but the access network and core network equipment between the optical cat and the Internet are provided by the operator and have nothing to do with the user.
There are also some third party speedtest websites and speed test apps that can be used to check internet speed. Remember to turn off video, download, and chat software when speed testing.