In recent years, oats have become a new representative of healthy cereals. For example, Oatmilk and oatmeal cereals have gradually appeared in the health food market as the main force. Of course, more studies have found that adding oats every day is related to reducing cholesterol and improving blood circulation. But before human beings planted so many oats and ate so many oats, they can't really understand it.
Until in a new nature paper, researchers from Australia cracked the genome of oats for the first time. They saw a lot about the special properties of oats, who are more suitable to eat oats, and even how oats can help improve diseases.

Modern oat is a hexaploid plant, which means that its genes are composed of three sub genomic sources, which have been provided by three wild oat species in the past 10 million years.
After the new study stripped the cocoon of the genome, it was found that oat contained more than 80000 genes, and there were frequent gene rearrangements, but the overall structure of the genome was similar to that of wheat and barley.

Through the analysis of these tens of thousands of genes, the researchers linked a single gene to the agronomic and nutritional characteristics of oats for the first time. For example, compared with wheat, oats rarely cause allergies or digestive intolerance.
According to the analysis of the new study, the protein content corresponding to wheat gluten in oats is very low, which means that eating oats can reduce celiac disease and other related symptoms caused by gluten protein. "In addition, we confirmed at the gene and protein levels that oats contain fewer gene sequences that may cause food allergy and intolerance," said Professor Michelle Colgrave, who participated in the study.
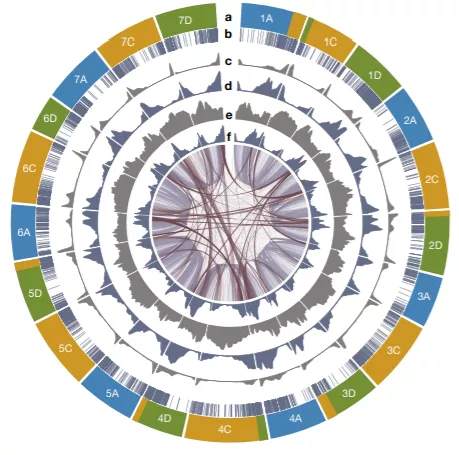
Moreover, the genes encoding negative glutenin sequences in oats are rare, or the expression level is very low, so eating oats is basically unlikely to cause physical inflammation.
Oats also contain a higher proportion of sugar than other grains β- Glucan, a substance that can reduce cholesterol levels in the blood, has a positive effect on patients with diabetes and metabolic diseases.
The researchers believe that these results suggest that oats may be safer to include in the gluten free food list, especially for patients with celiac disease. At present, these patients are strictly limited to this kind of food, and wheat and oats are excluded from the diet.
However, if you eat gluten free food for a long time, your whole grain intake will be very small, which is obviously related to the increased incidence rate of heart disease. If oats can be added to the gluten free food list, this situation can be greatly improved.
In addition to diet, oats can provide many benefits from agricultural planting. Oats require less pesticides and fertilizer than other grains. Now with the genome map of oats, scientists will be able to find genes with specific properties in the future, so as to solve the problems of breeding and protein production that may exist in other grain planting, and bring more healthy grain proteins to mankind.
"Barley is mainly used in the brewing process, while wheat is used to make flour and bread, but oats can be directly made into oatmeal for consumption, which is very close to the natural original grain," said Dr. Martin Mascher, one of the study authors. This may be one of the reasons why we should choose oats more.
reference material:
[1] Oat reference genome: Insights into a uniquely healthy cereal crop。 Retrieved May 19th , 2022 from https://www.eurekalert.org/news-releases/953108
[2] The mosaic oat genome gives insights into a uniquely healthy cereal crop。 Nature (2022)。 DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-04732-y